Lecture 10/10/2019, 9.30-11.00, Kolk
Learning goals
o Understanding of the basic mechanisms in neurodevelopment
o Understanding the embryological development of the nervous system, especially the brain
o Understanding the various (molecular) research approaches and strategies used by
(neuro)developmental biologists
o Recognize various structures of the developing brain
o Translate (mis)development into clinical signs
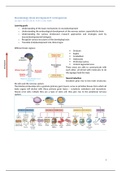
Different brain regions:
Striatum
Raphe
Cerebellum
Habenulae
Prefrontal cortex
Ventral tegmental area
These areas are able to communicate with
each other, all stirred with molecules to do
the signage (lead the way).
Neural induction
Ectoderm gives rise to two main structures:
the skin and the nervous system.
The blastocyst develops into a gastrula (primary germ layers, serve as primitive tissues from which all
body organs will derive) with three primary germ layers – ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm.
Neural crest cells: initially they are a type of stem cell, they give rise to the peripheral nervous
system.
1
,Human nervous system development
Image on the top right: The top layer is ectoderm. The dorsal neural groove
establishes the longitudinal axis of the embryo. At 23 days it seems open, but
this IS closed!
The neurulation process
Neurulation is the stage of organogenesis in vertebrate embryos, during which
the neural tube is transformed into the primitive structures that will later
develop into the central nervous system.
The process begins when the notochord induces the formation of the CNS by
signaling the ectoderm germ layer above it to form the thick and flat neural
plate. The neural plate folds in upon itself to form the neural tube, which will
later differentiate into the spinal cord and brain, eventually forming the CNS.
Neural induction can go wrong:
o Cystic hygroma = fluid-filled sac loacted in the neck or head area.
o Encephalocele = neural tube defect characterized by sac-like protrusions of the brain and
membranes that cover it through openings in the skull.
o Anencephaly = absence of a major portion of the brain.
o Spina Bifida
Polarity and Segmentation
These brain vesicles are important to remember (Tel Die
Mesen Met My).
2
, It slowly moves
towards each other,
that is also why it
bends.
Growth of cerebral
vesicles and
meninges.
Neurogenesis and migration
The overall length of the progenitor cell cycle increases during
embryogenesis.
The neuropregenitor cells will divide. They only divide close to the
ventricle.
Microcephaly and Megalencephaly
→ Human malformations due to proliferation/apoptosis defects.
A neurodevelopmental disorder in which the circumference of the head is more than two standard
deviations smaller than average for the person’s age and sex.
Microcephaly may be congenital or it may develop in the first few years of life. The disorder may
stem from a wide variety of conditions that cause abnormal growth of the brain, or from syndromes
associated with chromosomal abnormalities. → E.g. Intellectual disability.
Microcephaly can also be caused by a viral infection, e.g. the Zika virus.
3
, Image on the top left: The youngest neurons are in layer I and II, the oldest neurons are in layer VI.
Image on the top right: Radial migration in the cortex.
There are different types of migration in
cortical development
There can be human malformations due to
migration defects.
Almost all neurodevelopmental disorders have
parts of the brain where migration is distorted.
There are four possible scenarios in the NMDs:
1. Neurons don’t migrate at all from the ventricles (periventricular heterotopia) or migrate half
way (subcortical band heterotopia).
2. Some neurons reach the cortex but large numbers don’t. no normal cortical layers are
formed (lissencephaly).
3. Neurons over-shoot the cortex and end up in the subarachnoid space (cobblestone cortex).
4. The late stage of migration and cortical organization is disrupted (polymicrogyria).
Determination and differentiation
On the left, a neural progenitor left in tis normal environment
turns into a particular type of neuron.
In the middle, an intrinsically determined progenitor’s fate is
unchanged by transplantation to a different environment.
On the right, is an example of a progenitor whose fate is
determined extrinsically and so is changed by transplantation to
a different environment.
The fate is changed by host tissue. This can only happen with
neural progenitor cells, that are not yet intrinsically determined.
While they are still undetermined, they can be changed by the
environment.
4