metics , ,
DNA Replication
genome-complete set of DNA in a
living organism
·
genes-sequence of DNA that codes for specific proteins
·
·
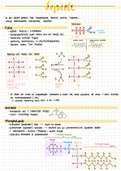
DNA replication to generate two identicle molecules from original DNA strand
① unwind helix
O add
complementary base
pairs
Reminders !
nucleotides linked
by phosphodiester bonds
·
are
·
phosphate group links carbon S' to carbon 3
nucleotides always added to 3' end
·
are
DNA replication steps
Qalarge protein binds to the
origin of replication,
DNA is unwound forming replication forks Singlerandeda
I >
leading
, -
② DNA helicase uses
energy from ATP hydrolysis >
-
strand
to unwind the DNA
③
single stranded binding proteins keep strands topioisomerase
-
apart lagging DNA he case
⑪ topoisomerate prevents
strand
twisting
Problem :
one side has a free 3' end ,
on doesn't
leading strand-free 3 end
↳
,
continuous replication
blagging strand-free S'end discontinuous replication
,
DNA Polymerase
moves sto 3
strand (Steps 5-7)
Leading ↑
>
-
⑤DNA polymerase requires a primer
Pet
synthesized by primace short RNA strand
↳
,
⑤ ⑮
③ DNA adds nucleotides to the 3 end
polymerase III
⑦ Primer is
degraded by DNA polymerasel and replaced
with DNA
, Lagging strand (Steps 5-8)
synthesized in fragments called Okazaki
·
fragments
⑤ each fragment needs its own
primerfrom
primase
⑤ DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to 3' ,
zi
end
mer
until reaching Primer of previous fragment
DNA polymerase then replaces primer
A Primase puts
with DNA polymerase
down primer
⑧ final phosphodiester link is created by
DNA
ligase
Transcription
·
Review the flow of information :
Replication only happens
:
during cell division MRNA
Translation
DNA Transcription :
RNA polypeptide
DNA sequence is RNA sequence acts as
2
Types
:
copied
RNA a template for an amino
to
complementary RNA noncodingto
:
a
·
coding Sequence acid sequence
noncoding rRNA
·
·
DNA
language
monomers
monomers for proteins amino acids
for DNA and RNA nucleotides transcribing
:
S to protein language
·
where does transcription occurs
the nucleus of the cell
↳ in
Transcription formation of specific RNA sequence from a specific DNA sequence
·
:
Requirements :
·
↳
a DNA template
"the four ribonucleoside triphosphates
:
ATP GTP CTP UTP
, , ,
↳
RNA
polymerase
↳
helper proteins
·
RNA (helper protein)
Polymerase
:
catalyzes addition of nucleotides to
growing mRNA in a
5 to 3 direction
↳ "DNA dependent" must read DNA to: build the RNA
only need one polymerase to bind
↳ all nucleotides to RNA
3 steps of transcription Initiation
Elongation Termination
·
:
, ,