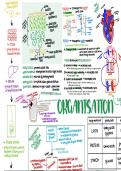
THE
-y
block of life wasy
PALOEM-> transports sug
ars
+EARL T
joram
↳ ~
L
cuticle -
and ious
-
W I :
⑧ cell - upper ↳ Translocation
SM-
--
-
pulmarters
onary
Iro
iname
↳ in both directions
S]
is
epider
L
robodie
-
=ligh
·
e
Li-onoem -I
heis
↓
--- - veins
D
palisade xylem
8
L
... ⑧ e
↑
-onloemcent
<
(mesophyUl
-
pulmone
·
sugars
⑧ (sucrose)
water
8 - xylem vessel atrium I
03
alls
033
I
moveable
·
·
⑧
⑧ -
D
mineral
·
DD ⑧
0
· ions
⑧
·D ⑧C ⑧
⑧
r
- spongy KYLEM ->
transports water-minerals
↳ TISSUE (mesophyul -
⑧ celle ↳ unidirectional (water moves Up the plant)
-
LUNGS
area↳Ber canad
-group of cells w/
shared function
>
00
⑧⑧
Lower epidermis
↳ Transpiration ->
movementof water." aeate e M -
~
oxygena
↑ * leaves through stomata .
StomaltaI guard
waxycuticle
↓ cells FACTORS affectingthe RATE TRANSPIRATION :
1) increase intemp . > increases rate
⑪
waxy cuticle prevents water loss More thermal energy transferred to water allowing it to evaporate quicker
:
↳
upper epidermis transparent
to allow
light to pass 2) increased light intensity increases rate
:
↳ Causes stomata to open
palisade cells main site of photosynthesis
:
3) faster air movement -> increases rate
↳ ORGAN air spaces allow gases to diffuse
spongy cells :
↳ Will blow away water vapour + distributes humidity in the air
allowing more to diffuse out
-group of tissues
t
guard cells sensitive to light-water open/close
:
increase in humidity -> decreases rate
;
4)
stomata
w/ shared function ↳ As the air will contain more water vapour, the concentration gradient
ribosomes synthesis protein ADAONSOROOTHAIRCELLS for diffusion is lower, making water unlikely transpire
-
energy
⑱
& -transport
releases 2 CIRC
⑰
Soractive lotsy stores water + minerals
5
vacuole
I
--- :
S *.
mitochondria
: M #
- + keeps cell turgid
S
·
.
↳
nucleus
- -
-
X
L
w
-
&
long finger-like projection
croot hair)
is
/
↳ increases S/A to absorb
w
water minerals from soil
acis
fatty
teeth (chec
a ⑲
+
mouth breakdown
Al ↳ mechanical
~
SCH
-M
-S -M
THEI a ↳ increases/A of bolus
secrete saliva
starch)
e
+
↳ ORGAN SYSTEM EW ↳ amylase (digest
If
D ~
↳
S
group of cegans working
-
oesophagus
together to carry out a
D
as
->
↳ peristalsis
bodily function
AC (p# 1/2)
carb
adach
Secretion ( STARCH
proteins digested
+
+
glucose
↓
↳ kill bacteria
by pepsina food
(proteasel ,
muscular tissue-churns
/mechanical
, ⑱
Food Tests
BIO M2 - RPA.4
AM
:
Use qualitative reagents to test for a range of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins
METHODS :
① Benedict's test for simple sugars :
• Add 2cm- of liquid food sample to a test tube
•8
•
•·
i Add 1cm of Benedict’s reagent to the test tube
Place the tube in an 80 C water bath
·
Check for positive result = blue brick-red (simple sugars present).
-
② lodine test for starch :
• Add few drops of iodine to either a dry or liquid food sample
⑱
• Check for positive result = orange-blue/black (starch present)
·
③ Biurettest for proteins :
• Add a few drops of Biuret reagent to liquid food sample
⑧
• Check for positive result = blue lilac (protein present)
->
④
⑧
Emulsion test for Lipids :
• To a liquid food sample, add a few drops of water then a few drops of ethanol
•⑧ " Secure test tube with a bung and shake the tube.
•P 3) Check for positive result = cloudy layer (lipids present)
HAZARDS/RISKS :
Iodine can stain surfaces
i Biuret reagent is an irritant
Ethanol is highly flammable
water bath will be hot