1.1WHAT IS MARKETING?
Marketing is a social and managerial process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need
and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others.
= build and maintain profitable customer relationships with stakeholders
Exchange obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something in return
2 parties
Something of value to offer
Want to deal with each other
Customer value: how much a product or service is worth to a customer
Benefits?
Costs?
Perceived value?
Applications marketing:
Physical products
Services
Retail
Experiences
Events
Film, music, theatre
Places
Ideas
Charities & non-profits
People
anywhere buyers have a choice
1.2WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CUSTOMERS AND CONSUMERS?
Consumers’ buying roles
1.3MARKET ORIENTATION
1
,= a strategic focus on identifying consumer needs and desires in order to define new products to be
developed
Definition: “The organization-wide generation of market intelligence pertaining to current and future customer
needs, dissemination of the intelligence across the departments, and organization-wide responsiveness to it”
(Kohli and Jaworski, 1990: 6).
▪ Organisation-wide belief in delivering customer value
▪ Understanding consumer needs even better than consumers themselves do
▪ Creating products that meet existing and latent needs, now or in the future
e.g., cars instead of faster horses
2
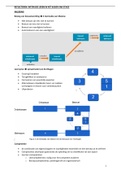
,The 3 components of market orientation
Customer orientation
Developing and redeveloping offerings to meet customer
needs. So, we should measure customer satisfaction on a
continuous basis and train our service staff
Competitor orientation
understanding of its competitors’1 short-term strengths and
weaknesses, and its own long-term capabilities and strategies
Interfunctional coordination
requiring all an organization’s functions to work together for
long-term profit growth
Customer centricity
= you put the customer at the centre of everything you do
→ try NOT to please ALL customers because it is impossible
1.4MARKETING’S INTELLECTUAL ROOTS
Industrial economics influences
. Supply and demand (price, quantity)
. Theories of income distribution, scale of operation, monopoly, competition, …
Psychological influences
. Consumer behaviour, motivation research, information processing
. Persuasion2, consumer personality, customer satisfaction, …
Sociological influences
. How groups of people behave: Demographics, class, motivation, customs, culture
. How communication passes through opinion leaders, …
Anthropological influences
. Qualitative approaches in researching consumer behaviour
Computer science influences
. Digitization, recommendation systems, apps, …
1.5DIFFERENCES BETWEEN SALES AND MARKETING
Marketing Sales
long-term satisfaction short-term satisfaction
greater input into customer design of offering lesser input into customer design of offering
high focus on stimulation of demand low focus on stimulation of demand
More focused on meeting existing demand
United colors of Benetton
Sales: Product push, short-term focus on satisfaction of customer needs Marketing:
Product pull, long-term focus on satisfaction of customer needs, high focus on
stimulation of demand
ZARA
3
, 1 concurrenten
2 overtuiging
4