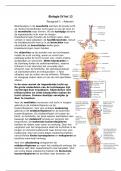
Suprascapular Nerve
o Arises from C6 and C7 spinal cord segments.
o Injury occurs most commonly when a horse’s shoulder is impacted
at speed, injuring the nerve as it curls around the front of the neck
of the scapula.
o Immediate laxity and lateral instability of the shoulder joint, causing
it to bow out or "pop" as the affected limb bears weight.
o Obvious atrophy of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles
within 2 to 4 weeks of injury.
o At least 50% of injuries are predominantly neurapraxic, and
recovery of function and muscle mass is evident within 30 days and
complete within 60 days.
o In more severe injuries with axonal damage, successful
reinnervation is evident as recovery of muscle bulk in the ventral
part of the supraspinatus muscle within 3 months of injury.
o Maximal recovery takes an additional 3 to 12 months.
o Regrowth of the suprascapular nerve can be facilitated by surgery
to resect scar tissue and reduce tension on the nerve (performed 3
to 6 months after injury).
o Removal of a piece of bone from the neck of the scapula may
further relax the nerve but can create a risk of scapular fractures
during anesthesia recovery.
Radial Nerve
o Innervates a flexor of the shoulder and extensors of the elbow,
carpal, and digital joints.
o Arises from T1.
o Can be lacerated by fractures of the C7 or T1 vertebrae or the first
rib.
o Commonly damaged by humeral fractures or trauma to the shoulder
region.
o Ischemic damage may occur in horses anesthetized in lateral
recumbency.
o Complete radial paralysis causes the shoulder to extend, the elbow
to "drop," and the dorsum of the hoof to rest on the ground.