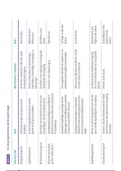
Material:
Period 1 (1492-1607) - Europeans Make Claims in the Americas
Module 1.1-Native American Societies before European Contact
- Usually permanent settlements in tribes closer towards Central America, they were able to
cultivate crops like maize and beans and support larger populations in their tribes with those crops
- One group of this were the Aztecs who built city-states in their tribe, had enough
resources to use, etc.
- Tribes more towards the North like the Incas or Ute did not form as many permanent settlements,
they depended on hunting and gathering for food, those living in mountain or rocky regions often
traveling for food. They were able to build bureaucratic empires, rely on domesticated animals
and diverse farming techniques to survive.
- Some tribes engaged in trading with others, trading fur, animals, goods, fish, etc..
Module 1.2-Portugal and Spain Expand their Reach
- Many of the reasons Spain chose to travel west and eventually colonize Central America were to
have a closer market with Asia, as their path through the Middle East was blocked by muslims
and those who could raid their traveling carts, they sought to expand the influence of the Catholic
Church, developed caravels, mariners, and astrolabes to guide them during adventures
- The Spanish led an inquisition starting in 1478 that eventually reached the Americas; as a result,
many of the cultures and beliefs of Native Americans were rejected, eliminated, and were made
out to be evil, savage, and contrary to those of Spain.
- As populations expanded to the Americas, Spaniards and Portuguese were able to develop more
efficient taxation, agricultural, and military systems
Module 1.3-Columbian Exchange, Spanish Exploration and Conquest
- Items traded between Euroepans, specifically the Spanish and Native American forces included
diseases, domesticated animals, corn, gold, wheat, rye, machinery and manufactured military
weapons, beans, sugar, etc. This trade was known as the Columbian Exchange, the biological
exchange between Native Americans and the rest of the world.
- Elite Europeans began to use the labor of Native Americans and Africans to extract previous
natural resources and create staple crops like sugar
- As Europe had previously owned slaves from Africa to support own systems back home, they
expanded that slave trade to the Americas during their exploration and conquest, shipping slaves
from ports along the West Coast of Africa to Europe to be traded back for goods. During this,
they developed and enacted laws that limited many freedoms and civil liberties enslaved people
initially had
- Systems of Feudalism began to include Africans and Native Americans as it had began being
enacted in the Americas, as a result of the Columbian Exchange and presence of more Native
Americans in Europe, etc.
- Feudalism eventually became replaced with the system of capitalism in the Americas, a system
based on private ownership of property and open exchange of goods between property holders →
encomienda system…
- The rise of capitalism was initiated by the increase in goods to Europe, the expansion overseas,
exploitation of Native American goods and those in Africa, and the influx of precious metals like
gold and silver to Europe. Even mercantilist principles that centered around accumulating wealth
from state-controlled monopolies..
,Module 1.4-Spanish Colonial Society
- Encomienda system centred around capitalism began to be enacted in the Americas; it allowed
encomiendas (leading men) to obtain land in the Americas and granted them the ability to demand
unpaid labor and tribute from all Native Americans living on that land
- The ability to claim land and protest priests in the Americas was granted by the Pope,
they felt a justification to do such actions
- The Spanish began to establish guidelines on taxation and social class based on ethnicity and
quality of Spanish education, placing Native Americans and Africans at the bottom of the Spanish
caste system as they had never been directly introduced to Spanish education. Higher taxes for
lower classes and lower for higher classes benefited the people who created that system as the
lower classes always had to pay tribute and did not have enough resources or funds to pay all
taxes
Module 1.5-Cultural Interactions among Europeans, Native Americans and Africans
- Spain’s global empire declined as they introduced the missionary system and forced Native
Americans and others to convert to Christianity, their attempts to extract wealth left tribes like
Pueblo unstable, starved, etc. leading to the Pueblo Revolt against the Spanish that forced settlers
to retreat from villages..
- Spain’s own division among the moral costs of colonization in the Americas left them a bit weak
in expansion to the North Americas…
- Pueblo Revolt in Northern territories led to Spain’s declining influence and expansion to the
North, although they claimed Texas…
Key Terms:
- Atlantic World: Interactions between the people of the lands bordering the Atlantic Ocean (Europe,
Africa and the Americas)
- Aztecs: Mexica, an indigenous people and empire of the same name, comprising a network of city-states,
that fell after the arrival of the Spaniards.
- Capitalism: Economic system based on private ownership of property and the open exchange of goods
between property holders
- Columbian Exchange: Biological exchange between the Americas and the rest of the work between
1492 and the end of the 1500s.
- Conquistadors: Spanish explorers and soldiers who led military expeditions in the Americas and
conquered indigenous empires, such as the Aztecs and Incas, in the 16th century.
- Encomienda: A Spanish labor system where colonists were granted the right to extract labor and tribute
from Indigenous peoples in exchange for providing protection and religious instruction. This system often
led to exploitation and harsh treatment.
- Feudalism: A medieval European social and economic system in which land was owned by lords who
allowed peasants to work the land in exchange for military protection and a share of the produce.
- Horticulture: The practice of garden cultivation and management, particularly by early Native American
societies, involving the growing of crops like maize, beans, and squash.
- Inquisition: Religious judicial institution designed to find and eliminate beliefs that did not align with
official catholic practices
- Missionary System: Organizational system established by the Spanish in 1573 in which Catholic
missionaries, rather than soldiers, directed all new settlements in the Americas
- Pueblo: Native American communities, particularly in the Southwestern United States, known for their
adobe and stone buildings, complex societies, and agricultural practices. The term also refers to the people
themselves.
, - Renaissance: A period of cultural, artistic, and intellectual revival in Europe from the 14th to the 17th
century, marked by a rediscovery of classical knowledge and advancements in art, science, and thought.
- Spanish Caste System: system developed by the Spanish in the 1500s that defined the status of diverse
populations based on a racial hierarchy that privileged Europeans.
- Staple Crops: Essential crops that are the basis of a region's diet or economy, such as tobacco, rice, and
sugar in the American colonies.
- Tenochtitlan: The capital city of the Aztec Empire, located on an island in Lake Texcoco, which was the
largest and most powerful city in Mesoamerica until its fall to the Spanish in 1521.
- Three Sisters: Farming technique that included corn, beans and squash all grown together.
Key Concepts Period 1:
1) Explain how geographic and environmental factors shaped Indigenous communities.
Indigenous communities throughout the Americas different in development because of their geographical and
environmental factors. Towards Central America hot climates and humidity made it easier to grow staple crops like
the three sisters (corn, beans and squash), so people did not have to go out and hunt for food and were able to build
more sedentary settlements, create city-states and live a more stable life. Three groups arose in Central America, the
Maya, Incas and Aztecs. Each of these groups had similar ways of growing agriculture, they developed language
and technologies off of each other, and established large capitals and city-states. Towards the Pacific Northwest,
American Indians lived more nomadic lives, hunting in forests, depending on fishing techniques, building canoes
and settling down in villages with homes made out of cedar and wood. In the Northeast, the Iroquois lived in
semi-sedentary villages, also building houses out of surrounding wood and they were also able to use the three
sisters technique. In the Great Basin/Great Plains drought and non-fertile land caused these groups to live
nomadically, they could not grow many crops, and they became very dependent on hunting, using bow and arrow
techniques and trading with other groups.
2) Explain how European economic and military competition led to the exploration and
colonization of the New World.
European economic and military competition played a significant role in driving exploration and colonization of the
New World during the 15th and 16th centuries. Motivated by mercantilism, European nations like Spain, Portugal,
France, and England sought to expand their wealth and power by acquiring new territories and resources.
Mercantilist theory emphasized accumulating wealth, particularly gold and silver, and controlling trade routes to
maintain a favorable balance of trade. As a result, nations competed to explore unknown lands in search of precious
metals, spices, and other commodities. Spain, for example, sponsored Christopher Columbus' voyages to find a
western route to Asia, which ultimately led to the discovery of the Americas. Similarly, Portugal, under the
leadership of Prince Henry the Navigator, aimed to explore new sea routes around Africa to establish trade
connections with Asia. This rivalry extended into military competition, as European powers vied to control valuable
colonies and defend them from other European rivals. The Treaty of Tordesillas (1494) is a prime example of this
competition, as Spain and Portugal divided the non-European world between them to avoid conflict over their
overseas claims. Colonization became a tool to assert dominance, extract resources, and establish profitable trade
routes, ultimately shaping the geopolitical landscape of the New World.
3) Explain how patterns of trade, including technology, food stuffs, and livestock, changed
and developed during the Columbian Exchange, and the ways Europeans and Indigenous
peoples interacted with these changes and the effects on both cultures.
New technology such as mariners, caravels, astrolabes, etc. made it easier for Europeans to trade and navigate
when traveling to Africa and the Americas. The development of weapons and guns were valued by the American
Indians, so they established a system of trade with the Europeans as a result. Unfortunately, with more people,
animals and unfamiliar goods coming to the Americas, disease and illness like smallpox spread very quickly among
the Indigenous People and decimated the population, resulting in the Great Dying. The introduction of new foods
Period 1 (1492-1607) - Europeans Make Claims in the Americas
Module 1.1-Native American Societies before European Contact
- Usually permanent settlements in tribes closer towards Central America, they were able to
cultivate crops like maize and beans and support larger populations in their tribes with those crops
- One group of this were the Aztecs who built city-states in their tribe, had enough
resources to use, etc.
- Tribes more towards the North like the Incas or Ute did not form as many permanent settlements,
they depended on hunting and gathering for food, those living in mountain or rocky regions often
traveling for food. They were able to build bureaucratic empires, rely on domesticated animals
and diverse farming techniques to survive.
- Some tribes engaged in trading with others, trading fur, animals, goods, fish, etc..
Module 1.2-Portugal and Spain Expand their Reach
- Many of the reasons Spain chose to travel west and eventually colonize Central America were to
have a closer market with Asia, as their path through the Middle East was blocked by muslims
and those who could raid their traveling carts, they sought to expand the influence of the Catholic
Church, developed caravels, mariners, and astrolabes to guide them during adventures
- The Spanish led an inquisition starting in 1478 that eventually reached the Americas; as a result,
many of the cultures and beliefs of Native Americans were rejected, eliminated, and were made
out to be evil, savage, and contrary to those of Spain.
- As populations expanded to the Americas, Spaniards and Portuguese were able to develop more
efficient taxation, agricultural, and military systems
Module 1.3-Columbian Exchange, Spanish Exploration and Conquest
- Items traded between Euroepans, specifically the Spanish and Native American forces included
diseases, domesticated animals, corn, gold, wheat, rye, machinery and manufactured military
weapons, beans, sugar, etc. This trade was known as the Columbian Exchange, the biological
exchange between Native Americans and the rest of the world.
- Elite Europeans began to use the labor of Native Americans and Africans to extract previous
natural resources and create staple crops like sugar
- As Europe had previously owned slaves from Africa to support own systems back home, they
expanded that slave trade to the Americas during their exploration and conquest, shipping slaves
from ports along the West Coast of Africa to Europe to be traded back for goods. During this,
they developed and enacted laws that limited many freedoms and civil liberties enslaved people
initially had
- Systems of Feudalism began to include Africans and Native Americans as it had began being
enacted in the Americas, as a result of the Columbian Exchange and presence of more Native
Americans in Europe, etc.
- Feudalism eventually became replaced with the system of capitalism in the Americas, a system
based on private ownership of property and open exchange of goods between property holders →
encomienda system…
- The rise of capitalism was initiated by the increase in goods to Europe, the expansion overseas,
exploitation of Native American goods and those in Africa, and the influx of precious metals like
gold and silver to Europe. Even mercantilist principles that centered around accumulating wealth
from state-controlled monopolies..
,Module 1.4-Spanish Colonial Society
- Encomienda system centred around capitalism began to be enacted in the Americas; it allowed
encomiendas (leading men) to obtain land in the Americas and granted them the ability to demand
unpaid labor and tribute from all Native Americans living on that land
- The ability to claim land and protest priests in the Americas was granted by the Pope,
they felt a justification to do such actions
- The Spanish began to establish guidelines on taxation and social class based on ethnicity and
quality of Spanish education, placing Native Americans and Africans at the bottom of the Spanish
caste system as they had never been directly introduced to Spanish education. Higher taxes for
lower classes and lower for higher classes benefited the people who created that system as the
lower classes always had to pay tribute and did not have enough resources or funds to pay all
taxes
Module 1.5-Cultural Interactions among Europeans, Native Americans and Africans
- Spain’s global empire declined as they introduced the missionary system and forced Native
Americans and others to convert to Christianity, their attempts to extract wealth left tribes like
Pueblo unstable, starved, etc. leading to the Pueblo Revolt against the Spanish that forced settlers
to retreat from villages..
- Spain’s own division among the moral costs of colonization in the Americas left them a bit weak
in expansion to the North Americas…
- Pueblo Revolt in Northern territories led to Spain’s declining influence and expansion to the
North, although they claimed Texas…
Key Terms:
- Atlantic World: Interactions between the people of the lands bordering the Atlantic Ocean (Europe,
Africa and the Americas)
- Aztecs: Mexica, an indigenous people and empire of the same name, comprising a network of city-states,
that fell after the arrival of the Spaniards.
- Capitalism: Economic system based on private ownership of property and the open exchange of goods
between property holders
- Columbian Exchange: Biological exchange between the Americas and the rest of the work between
1492 and the end of the 1500s.
- Conquistadors: Spanish explorers and soldiers who led military expeditions in the Americas and
conquered indigenous empires, such as the Aztecs and Incas, in the 16th century.
- Encomienda: A Spanish labor system where colonists were granted the right to extract labor and tribute
from Indigenous peoples in exchange for providing protection and religious instruction. This system often
led to exploitation and harsh treatment.
- Feudalism: A medieval European social and economic system in which land was owned by lords who
allowed peasants to work the land in exchange for military protection and a share of the produce.
- Horticulture: The practice of garden cultivation and management, particularly by early Native American
societies, involving the growing of crops like maize, beans, and squash.
- Inquisition: Religious judicial institution designed to find and eliminate beliefs that did not align with
official catholic practices
- Missionary System: Organizational system established by the Spanish in 1573 in which Catholic
missionaries, rather than soldiers, directed all new settlements in the Americas
- Pueblo: Native American communities, particularly in the Southwestern United States, known for their
adobe and stone buildings, complex societies, and agricultural practices. The term also refers to the people
themselves.
, - Renaissance: A period of cultural, artistic, and intellectual revival in Europe from the 14th to the 17th
century, marked by a rediscovery of classical knowledge and advancements in art, science, and thought.
- Spanish Caste System: system developed by the Spanish in the 1500s that defined the status of diverse
populations based on a racial hierarchy that privileged Europeans.
- Staple Crops: Essential crops that are the basis of a region's diet or economy, such as tobacco, rice, and
sugar in the American colonies.
- Tenochtitlan: The capital city of the Aztec Empire, located on an island in Lake Texcoco, which was the
largest and most powerful city in Mesoamerica until its fall to the Spanish in 1521.
- Three Sisters: Farming technique that included corn, beans and squash all grown together.
Key Concepts Period 1:
1) Explain how geographic and environmental factors shaped Indigenous communities.
Indigenous communities throughout the Americas different in development because of their geographical and
environmental factors. Towards Central America hot climates and humidity made it easier to grow staple crops like
the three sisters (corn, beans and squash), so people did not have to go out and hunt for food and were able to build
more sedentary settlements, create city-states and live a more stable life. Three groups arose in Central America, the
Maya, Incas and Aztecs. Each of these groups had similar ways of growing agriculture, they developed language
and technologies off of each other, and established large capitals and city-states. Towards the Pacific Northwest,
American Indians lived more nomadic lives, hunting in forests, depending on fishing techniques, building canoes
and settling down in villages with homes made out of cedar and wood. In the Northeast, the Iroquois lived in
semi-sedentary villages, also building houses out of surrounding wood and they were also able to use the three
sisters technique. In the Great Basin/Great Plains drought and non-fertile land caused these groups to live
nomadically, they could not grow many crops, and they became very dependent on hunting, using bow and arrow
techniques and trading with other groups.
2) Explain how European economic and military competition led to the exploration and
colonization of the New World.
European economic and military competition played a significant role in driving exploration and colonization of the
New World during the 15th and 16th centuries. Motivated by mercantilism, European nations like Spain, Portugal,
France, and England sought to expand their wealth and power by acquiring new territories and resources.
Mercantilist theory emphasized accumulating wealth, particularly gold and silver, and controlling trade routes to
maintain a favorable balance of trade. As a result, nations competed to explore unknown lands in search of precious
metals, spices, and other commodities. Spain, for example, sponsored Christopher Columbus' voyages to find a
western route to Asia, which ultimately led to the discovery of the Americas. Similarly, Portugal, under the
leadership of Prince Henry the Navigator, aimed to explore new sea routes around Africa to establish trade
connections with Asia. This rivalry extended into military competition, as European powers vied to control valuable
colonies and defend them from other European rivals. The Treaty of Tordesillas (1494) is a prime example of this
competition, as Spain and Portugal divided the non-European world between them to avoid conflict over their
overseas claims. Colonization became a tool to assert dominance, extract resources, and establish profitable trade
routes, ultimately shaping the geopolitical landscape of the New World.
3) Explain how patterns of trade, including technology, food stuffs, and livestock, changed
and developed during the Columbian Exchange, and the ways Europeans and Indigenous
peoples interacted with these changes and the effects on both cultures.
New technology such as mariners, caravels, astrolabes, etc. made it easier for Europeans to trade and navigate
when traveling to Africa and the Americas. The development of weapons and guns were valued by the American
Indians, so they established a system of trade with the Europeans as a result. Unfortunately, with more people,
animals and unfamiliar goods coming to the Americas, disease and illness like smallpox spread very quickly among
the Indigenous People and decimated the population, resulting in the Great Dying. The introduction of new foods