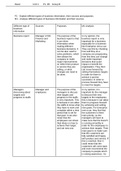
Functional Supervision
- Workers are supervised by people with expertise in their area
Specialization
- Refers to division of labor/job differentiation
- Police executive must divide the work for efficiency
( function, geography, time, level of authority, functional specialization )
Scientific management
- By frederick taylor ( 1865-1915 )
- a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflows.
( focus effort on employees )
- Goal was to provide orderly manner to work; for worker and
manager to cooperate
Theorist
Maslo :
- Maslow's theory was the psychological well-being of individuals was
dependent on fulfilling their needs in order of priority. Humans are
motivated when their needs are fulfilled.
- Based on basic survival, safety, belongingness, ego status, and self-
actualization
McGregor Douglas :
- Had the X & Y Theory
- X theory implied that managers must constantly control, punish and
manipulate employees
- Y theory implied that workers willingly failed work and
productiveness when management fails to provide a proper
atmosphere.
Hawthorn:
- produced by mayo and it showed that if management paid more
attention to the workers than more things would get done. This
benefitted both parties
Classical organization theory:
- theory includes the scientific management approach, Weber's
bureaucratic approach, and administrative theory
- achieve efficiency, standardization, specialization and simplification.
- seven classical principles of organization
( specialization, authority and responsibility, discipline, unity of command,
the scalar chain, centralization, and the paramilitary model. )
- Workers are supervised by people with expertise in their area
Specialization
- Refers to division of labor/job differentiation
- Police executive must divide the work for efficiency
( function, geography, time, level of authority, functional specialization )
Scientific management
- By frederick taylor ( 1865-1915 )
- a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflows.
( focus effort on employees )
- Goal was to provide orderly manner to work; for worker and
manager to cooperate
Theorist
Maslo :
- Maslow's theory was the psychological well-being of individuals was
dependent on fulfilling their needs in order of priority. Humans are
motivated when their needs are fulfilled.
- Based on basic survival, safety, belongingness, ego status, and self-
actualization
McGregor Douglas :
- Had the X & Y Theory
- X theory implied that managers must constantly control, punish and
manipulate employees
- Y theory implied that workers willingly failed work and
productiveness when management fails to provide a proper
atmosphere.
Hawthorn:
- produced by mayo and it showed that if management paid more
attention to the workers than more things would get done. This
benefitted both parties
Classical organization theory:
- theory includes the scientific management approach, Weber's
bureaucratic approach, and administrative theory
- achieve efficiency, standardization, specialization and simplification.
- seven classical principles of organization
( specialization, authority and responsibility, discipline, unity of command,
the scalar chain, centralization, and the paramilitary model. )