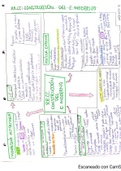
Interpretation Assessment
4 unique components of cardiac cells - conductivity, excitability, automacity, contractility
conductivity - the ability to transfer an electrial impulse quickly
-calcium-sodium-potassium-magnesium
excitabilty - tyhe ability to respond to a stimulus
automaticity - the heart can run its own electrial conduction system
contractility - the actual mechanical movement of the cardiac muscle
layers of the heart - epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
-high calcium: irritable heart
-low calcium: low electrical current, delayed conduction
action potential - •Mvmt of ions across cell membrane causes electrical impulse that stimulates muscle
contraction
deploarization - •When cell stimulated by an electrical impulse, Na+ rushes into the cell and K+ leaks out
causing cell to become + charged.
repolarization - •During cell recovery, ions shift back to their original places and return the cell to
negative
electrical conduction through the heart - SA node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, and
Purkinje fibers
, pacemaker cells - -the fastest pacemaker at any given moment is the one in control
-SA node: 60-100
-AV node 40-60
-Ventricle: 20-40
-if SA node fails, AV node takes over and etc
sinus rhythm - if there is a p wave for every QRS
ST segment - -what you look at in MI, tombstone (ST segment elevation)
peaked T wave - -caused by hyperkalemia
U wave - -rarely seen, caused by hypokalemia
rhythm boxes - -small box is .04
normal EKG findings - -PR: .12-.20
-QRS: .06-.11
-ST: isoelectric
-T wave: round and upright
-QT: 0.32-0.44
-Isoelectric means, equal with baseline
Heart rate - -little block method; count the # of little squares between R's, then take it out of 1500
big block method - count # of big blocks between 2 consecutive r waves and divide 300 by that #
ex) ,1 = 73