Solutions
Save
Practice questions for this set
Learn 1 /7 Study with Learn
K/Ar T1/2 = 1.3 by
14C T1/2 = 5,730 y
Choose an answer
1 Weathering 2 isotopic dating systems
3 chemical sedimentary rocks 4 Weathering factors
Don't know?
Terms in this set (49)
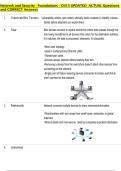
the chemical alteration and physical breakdown of rock
Weathering material during exposure to the air, moisture, and
organic matter.
development of joints, crystal growth(salts), frost-
wedging/freeze-thaw, heat (spalling and thermal
Mechanical weathering
expansion/contraction), bioturbation (root penetration
and enlarging joint fractures in rock)
, Chemical weathering carbonation, hydrolisis, oxidation, dissolution
Weathering effects on concentration of stable minerals, weathering rinds,
rocks spheroidal weathering
Weathering factors climate, organisms, relief, parent material, time
eluviation (removal), illuviation (accumulation),
translocation (movement of material through soil
Soil formation
profile), transformation (chemical alteration of minerals
within soil profile in situ)
climate, organisms, relief, parent material, time
Factors of soil formation
(CLORTP)
O: loose organic matter
A: Inorganic matter w/humus; constantly cycling; topsoil
E: eluviated horizon, little/no organic matter
SOIL
B: zone of illuviation containing materials from zone of
accumulation (E)
C: weathered parent material, little to no organic matter
w: accumulation of iron oxide
wk
k: calcium carbonate
sedimentary rock formation accumulation, compaction, cementation
cementing agents Silica, Fe-oxide, Calcite, Clays, and Tar
accumulated particles of broken rock or skeletal
clastic sedimentary rocks remains of dead organisms.
conglomerate, sandstone, siltstone, mudstone (shale)
formed by precipitation of minerals from solution in
chemical sedimentary rocks water.
limestone, dolostone, rock salt
refers to changes that affect sediment after its initial
deposition.
diagenesis
compaction, cementation, recrystalization, oxidation,
reduction
topset beds: uppermost layer
foreset beds: middle layer(slightly coarser deposited
deltaic structures
material)
bottomset beds: lowest part of delta, fine material
relative dating determining the chronological order of events