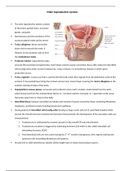
Male reproductive system
The male reproductive system consists
of the testes, genital ducts, accessory
glands, and penis
Spermatozoa and the secretions of the
accessory glands make up the semen
Tunica albuginea: dense connective
tissue that surrounds the testis. It
thickens on the posterior side to form
the mediastinum testis.
Testicular lobules: separated by septa
(around 250 pyramidal compartments). Each lobule contains sparse connective tissue with endocrine interstitial
cells (Leydig cells) which secrete testosterone. It also contains 1-4 seminiferous tubules in which sperm
production occurs.
Tunica vaginalis: a serous sac that is carried with the testis when they migrate from the abdominal cavity to the
scrotum. It has parietal layer lining the scrotum and an inner visceral layer covering the tunica albuginea on the
anterior and lateral sides of the testis.
Papmpiniform venous plexus: surrounds each testicular artery and it contains cooler blood from the testis
which draws heat from the arterial blood. Dartos m. ( scrotum) and the cremaster m. ( spermatic cords) move
the testes away from or closer to the body.
Interstitial tissue: between seminiferous tubules and consists of sparse connective tissue containing fibroblasts,
lymphatics, and blood vessels including fenestrated capillaries.
During puberty Interstitial cells (Leydig cells) develop as large round cells rich in small lipid droplets which
secrete the steroid hormone testosterone (hormone that promotes the development of the secondary male sex
characteristics)
1. Testosterone is synthesized by enzymes present in the smooth ER and mitochondria.
2. Testosterone secretion is triggered by luteinizing hormone (LH) which is also called interstitial cell
stimulating hormone (ICSH)
3. Fetal interstitial cells are very active during the 3rd -4th months of pregnancy, then regress and become
quiescent cells resembling fibroblasts until puberty.
Around 250 to 1000 seminiferous tubules (250m length each) in testes that produces sperm.
, 4. Each tubule is linked by a straight
tubule to the rete testis which is a
labyrinth of epithelium-linked channels
embedded in the mediastinum testis
5. Efferent ductules connect the rete
testis to the head of the epididymis,
Each seminiferous tubule is lined with a
complex specialized stratified epithelium called
germinal or spermatogenic epithelium. Its
basement membrane has myoid cells which
allow weak contractions of the tubule. It
consists of 2 types of cells:
6. Sertoli cells: large nondividing cells
which physically and metabolically
support developing sperm cell precursors.
7. Spermatogenic lineage: dividing cells
Spermatogenesis begins at puberty with proliferation of stem and progenitor cells called spermatogonia.
8. Type A spermatogonia Type B spermatogonia after mitosis they become primary spermatocytes
after meiosis they become secondary spermatocytes with only 23 chromosomes instead of 46 (they
are rare in testis sections because they are very short-lived cells)after undergoing meiosis II, they
become spermatids
Spermiogenesis: final phase of sperm production and it is temperature-sensitive process by which spermatids
differentiate into spermatozoa which are specialized to deliver male DNA to ovum. It requires the
formation of the acrosome, condensation and elongation of the nucleus, development of the flagellum, and the
loss of much of the cytoplasm.
Its 4 stages are:
Golgi phase: small proacrosomal vesicles from the golgi apparatus coalesce as a single membrane-
limited acrosomal cap close to one end of the nucleus. The centrioles migrate to the farthest position
from acrosomal cap, and one acts as a basal body organizing the axoneme of the flagellum.
Cap phase: acrosomal cap spreads over half of the condensing nucleus. The acrosome is a specialized
type of lysosome containing hydrolytic enzymes (mainly hyaluronidase and a trypsin-like protease called
acrosin). The enzymes are released when a spermatozoon encounters an oocyte and the acrosomal
membrane fuses with the sperm’s plasma membrane.
Acrosomal reaction: one of the first steps in fertilization
The male reproductive system consists
of the testes, genital ducts, accessory
glands, and penis
Spermatozoa and the secretions of the
accessory glands make up the semen
Tunica albuginea: dense connective
tissue that surrounds the testis. It
thickens on the posterior side to form
the mediastinum testis.
Testicular lobules: separated by septa
(around 250 pyramidal compartments). Each lobule contains sparse connective tissue with endocrine interstitial
cells (Leydig cells) which secrete testosterone. It also contains 1-4 seminiferous tubules in which sperm
production occurs.
Tunica vaginalis: a serous sac that is carried with the testis when they migrate from the abdominal cavity to the
scrotum. It has parietal layer lining the scrotum and an inner visceral layer covering the tunica albuginea on the
anterior and lateral sides of the testis.
Papmpiniform venous plexus: surrounds each testicular artery and it contains cooler blood from the testis
which draws heat from the arterial blood. Dartos m. ( scrotum) and the cremaster m. ( spermatic cords) move
the testes away from or closer to the body.
Interstitial tissue: between seminiferous tubules and consists of sparse connective tissue containing fibroblasts,
lymphatics, and blood vessels including fenestrated capillaries.
During puberty Interstitial cells (Leydig cells) develop as large round cells rich in small lipid droplets which
secrete the steroid hormone testosterone (hormone that promotes the development of the secondary male sex
characteristics)
1. Testosterone is synthesized by enzymes present in the smooth ER and mitochondria.
2. Testosterone secretion is triggered by luteinizing hormone (LH) which is also called interstitial cell
stimulating hormone (ICSH)
3. Fetal interstitial cells are very active during the 3rd -4th months of pregnancy, then regress and become
quiescent cells resembling fibroblasts until puberty.
Around 250 to 1000 seminiferous tubules (250m length each) in testes that produces sperm.
, 4. Each tubule is linked by a straight
tubule to the rete testis which is a
labyrinth of epithelium-linked channels
embedded in the mediastinum testis
5. Efferent ductules connect the rete
testis to the head of the epididymis,
Each seminiferous tubule is lined with a
complex specialized stratified epithelium called
germinal or spermatogenic epithelium. Its
basement membrane has myoid cells which
allow weak contractions of the tubule. It
consists of 2 types of cells:
6. Sertoli cells: large nondividing cells
which physically and metabolically
support developing sperm cell precursors.
7. Spermatogenic lineage: dividing cells
Spermatogenesis begins at puberty with proliferation of stem and progenitor cells called spermatogonia.
8. Type A spermatogonia Type B spermatogonia after mitosis they become primary spermatocytes
after meiosis they become secondary spermatocytes with only 23 chromosomes instead of 46 (they
are rare in testis sections because they are very short-lived cells)after undergoing meiosis II, they
become spermatids
Spermiogenesis: final phase of sperm production and it is temperature-sensitive process by which spermatids
differentiate into spermatozoa which are specialized to deliver male DNA to ovum. It requires the
formation of the acrosome, condensation and elongation of the nucleus, development of the flagellum, and the
loss of much of the cytoplasm.
Its 4 stages are:
Golgi phase: small proacrosomal vesicles from the golgi apparatus coalesce as a single membrane-
limited acrosomal cap close to one end of the nucleus. The centrioles migrate to the farthest position
from acrosomal cap, and one acts as a basal body organizing the axoneme of the flagellum.
Cap phase: acrosomal cap spreads over half of the condensing nucleus. The acrosome is a specialized
type of lysosome containing hydrolytic enzymes (mainly hyaluronidase and a trypsin-like protease called
acrosin). The enzymes are released when a spermatozoon encounters an oocyte and the acrosomal
membrane fuses with the sperm’s plasma membrane.
Acrosomal reaction: one of the first steps in fertilization