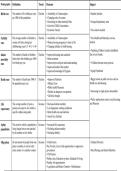
Demography Definition Trend Reasons Impact
Birth rate The number of live births per year Decline • Availability of Contraception • Smaller families
per 1000 of the population • Changing roles of women
• Decreasing in infant mortality Rate • Unequal dependency ratio
• Growth of Child Centeredness
• Economic Factors • Few schools needed
Fertility The average number of children a Decline • Availability of Contraception • Few Health and Maternity services
rate women will have during her • Women leaving pregnancy to later in life needed.
childbearing years (15 –45) = 1.44 • Changing attitudes to child bearing.
• Vanishing Children Lonelier childhood
Infant The number of deaths of children Decline • Improved housing and sanitation due to less friends.
mortality before their first birthday per 1000 • Better nutrition
rate live births per year. • Improved pre and post natal understanding • Children become more precious
• Improved health of the mother
• Improved knowledge of Hygiene. • Aging Population
Death rate The number of deaths per 1000 of Decline • Improved Nutrition • Bigger strain on public services such as
the population per year. • Medical Care health care and housing.
• Public health Measures
• Decline in dangerous occupations • Increasing in single person households
• Lifestyle changes
• Policy implications such as social housing
Life The average number of years a Increase • Decreased infant mortality and Pensions
expectancy person can expect to live within a • Less dangerous working conditions
specific culture and gender. • Better health care and nutrition
• Social Care facilities
Aging The extent to which a population is Increase • Increased life expectancy
population living longer but are not matched • Declining infant mortality
by the number of new births. • Declining fertility
Migration the movement of peoples from one Increase • Push Factors • Cultural Diversity
place to another, it can be in the War, Poverty, Lack of job opportunities or oppressive
same county or to another country government. • Duel Heritage and hybrid Identities
• Pull Factors
Welfare state, Education systems, Standard of living,
Weather, Job opportunities.
• Legislation and Border Controls • Globalisation
Birth rate The number of live births per year Decline • Availability of Contraception • Smaller families
per 1000 of the population • Changing roles of women
• Decreasing in infant mortality Rate • Unequal dependency ratio
• Growth of Child Centeredness
• Economic Factors • Few schools needed
Fertility The average number of children a Decline • Availability of Contraception • Few Health and Maternity services
rate women will have during her • Women leaving pregnancy to later in life needed.
childbearing years (15 –45) = 1.44 • Changing attitudes to child bearing.
• Vanishing Children Lonelier childhood
Infant The number of deaths of children Decline • Improved housing and sanitation due to less friends.
mortality before their first birthday per 1000 • Better nutrition
rate live births per year. • Improved pre and post natal understanding • Children become more precious
• Improved health of the mother
• Improved knowledge of Hygiene. • Aging Population
Death rate The number of deaths per 1000 of Decline • Improved Nutrition • Bigger strain on public services such as
the population per year. • Medical Care health care and housing.
• Public health Measures
• Decline in dangerous occupations • Increasing in single person households
• Lifestyle changes
• Policy implications such as social housing
Life The average number of years a Increase • Decreased infant mortality and Pensions
expectancy person can expect to live within a • Less dangerous working conditions
specific culture and gender. • Better health care and nutrition
• Social Care facilities
Aging The extent to which a population is Increase • Increased life expectancy
population living longer but are not matched • Declining infant mortality
by the number of new births. • Declining fertility
Migration the movement of peoples from one Increase • Push Factors • Cultural Diversity
place to another, it can be in the War, Poverty, Lack of job opportunities or oppressive
same county or to another country government. • Duel Heritage and hybrid Identities
• Pull Factors
Welfare state, Education systems, Standard of living,
Weather, Job opportunities.
• Legislation and Border Controls • Globalisation