A LEVEL ECONOMICS
NOTES
Evaluate whether increasing contestability improves economic efficiency in an industry of your choice.
Point 1: Increased allocative efficiency
Increasing contestability refers to the ease at which new firms can enter the market=
This means barriers to entry are falling and so this makes it easy for new firms to join the market=
In the supermarket industry, Aldi and Lidl were able to join the market and increase their market share
from around 10% in 2017 to 15% in 2022=
Lidl and Aldi were able to steal market share through lower prices attracting consumers and stealing
market share from large, dominant incumbent firms such as Tesco and Asda=
As a result of falling demand for dominant incumbent firms such as Tesco, their price-setting power
falls and thus they may have to lower their prices in order to avoid losing more market share=
As Lidl and Aldi operate with lower prices this is closer to allocative efficiency but also incumbent
firms lower prices in order to remain competitive and so firms in the supermarket industry operate
closer to allocative efficiency=
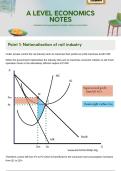
Allocative efficiency is when resources follow consumer demand and maximises consumer
satisfaction=
As a result, firms operate closer to P=MC and therefore prices rise and thus consumer welfare rises
and consumer surplus area rises
NOTES
Evaluate whether increasing contestability improves economic efficiency in an industry of your choice.
Point 1: Increased allocative efficiency
Increasing contestability refers to the ease at which new firms can enter the market=
This means barriers to entry are falling and so this makes it easy for new firms to join the market=
In the supermarket industry, Aldi and Lidl were able to join the market and increase their market share
from around 10% in 2017 to 15% in 2022=
Lidl and Aldi were able to steal market share through lower prices attracting consumers and stealing
market share from large, dominant incumbent firms such as Tesco and Asda=
As a result of falling demand for dominant incumbent firms such as Tesco, their price-setting power
falls and thus they may have to lower their prices in order to avoid losing more market share=
As Lidl and Aldi operate with lower prices this is closer to allocative efficiency but also incumbent
firms lower prices in order to remain competitive and so firms in the supermarket industry operate
closer to allocative efficiency=
Allocative efficiency is when resources follow consumer demand and maximises consumer
satisfaction=
As a result, firms operate closer to P=MC and therefore prices rise and thus consumer welfare rises
and consumer surplus area rises