2025/2026
Support - (answer)The structural function of bones that provides a framework for the body, allowing it
to maintain its shape and support the weight of muscles and organs.
Hematopoiesis - (answer)The process of blood cell production that occurs in the bone marrow, where
red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are formed.
Protection - (answer)The role of bones in safeguarding vital organs from injury, such as the skull
protecting the brain and the rib cage shielding the heart and lungs.
Mineral Storage - (answer)The function of bones in storing essential minerals, particularly calcium and
phosphorus, which can be released into the bloodstream as needed for various bodily functions.
Support - (answer)Provides a rigid framework that supports the body and cradles soft organs.
Protection - (answer)Safeguards vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs from injury.
Movement - (answer)Serves as attachment points for muscles, enabling movement through leverage.
Mineral Storage - (answer)Stores essential minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus, which can be
released into the bloodstream as needed.
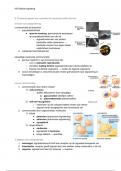
Periosteum - (answer)A strong fibrous membrane that covers the outer surface of long bones, providing
attachment for muscles and serving as a conduit for blood vessels and nerves.
Cortex - (answer)The outer layer of a bone, composed of dense and compact bone tissue that provides
strength and protection.
Medullary Cavity - (answer)The central cavity within long bones that contains bone marrow, which is
involved in the production of blood cells.
, The Human Body in Health and Disease 8th Edition by Patton Test Bank with Solution
2025/2026
Endosteum - (answer)A thin membrane lining the medullary cavity of a bone, involved in bone growth,
repair, and remodeling.
Articular Cartilage - (answer)A smooth, slippery tissue that covers the ends of bones at joints, reducing
friction and absorbing shock during movement.
Bone Marrow - (answer)A soft tissue found within the medullary cavity of bones, responsible for
producing blood cells and storing fat.
Trabecular Bone - (answer)Also known as spongy bone, this type of bone is characterized by a porous
structure and is found at the ends of long bones and in the interior of others.
Compact Bone - (answer)A dense and solid type of bone that forms the outer layer of bones, providing
strength and support.
Spongy Bone - (answer)A type of bone tissue characterized by a porous, lattice-like structure that
provides strength and support while being lighter than compact bone.
Trabeculae - (answer)The small, rod-like structures that make up the lattice framework of spongy bone,
helping to distribute stress and support the bone.
Osteocytes - (answer)Mature bone cells embedded within the bone matrix that help maintain bone
tissue.
Long Bone - (answer)A type of bone that is longer than it is wide, typically found in the limbs, and is
responsible for supporting weight and facilitating movement.
Short Bone - (answer)A type of bone that is approximately equal in length, width, and thickness,
providing stability and support with little movement, commonly found in the wrists and ankles.