Functions of the cardiovascular system include:
1. Transport of nutrients, water, and gasses that enter
the body from the external environment
2. Transport of materials from cell to cell
3. Transport of cell waste
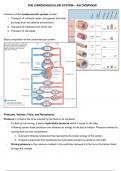
Basic composition of the cardiovascular system:
Pressure, Volume, Flow, and Resistance:
Pressure in a fluid is the force exerted by the fluid on its container.
- If a fluid is not moving, it exerts hydrostatic pressure which is equal on all sides.
- A flowing system loses pressure over distance as energy is lost due to friction. Pressure exerted by
moving fluid has two components:
1. A dynamic flowing component that represents the kinetic energy of the system
2. A lateral component that represents the hydrostatic pressure exerted on the walls
- Driving pressure is the pressure created in the ventricles because it is the force that drives blood
through the vessels
, - The pressure gradient (ΔP) is the difference in pressure between a high pressure and a low
pressure area. Flow is directly proportional to the pressure gradient, and it flows from higher to lower
pressure.
Resistance is the tendency of the cardiovascular system to oppose blood flow.
- Flow is inversely proportional to resistance
- Resistance in a tube is determined by the radius, the length of the tube, and the viscosity of the fluid
- Poiseuille’s law states that resistance is directly proportional to length and viscosity, and inversely
proportional to radius
- Since the length of the circulatory system remains constant, and the viscosity of blood (determined by
the ratio of RBCs to plasma and by how much protein is in the plasma) does not often fluctuate, the
main determinant is radius
4
- 𝑅 α 1/𝑟 where R is resistance and r is radius
- Vasoconstriction is a decrease in blood vessel diameter, while vasodilation is an increase in blood
vessel diameter
- Flow rate is the volume of blood that passes a given point in the system per unit time
- 𝑣 = 𝑄/𝐴 where Q is the flow rate and A is the cross-sectional area of the tube
,Anatomy of the heart
Cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle and shares some properties with smooth muscle:
1. Cardiac muscle fibers are much smaller than skeletal muscle fibers and usually have a single nucleus
per fiber.
2. They are connected by`, which consist of interdigitated membranes. They are composed of
desmosomes and gap junctions.
, 3. Gap junctions in the intercalated disks electrically connect cardiac muscle cells to one another. They
allow waves of depolarization to spread rapidly from cell to cell, so that all the heart muscle cells
contract almost simultaneously.
4. The t-tubules of myocardial cells are larger than those of skeletal muscle, and they branch inside the
myocardial cells.
5. Myocardial sarcoplasmic reticulum is smaller than that of skeletal muscle, reflecting the fact that
cardiac muscle depends in part on extracellular Ca2+ to initiate contraction.
EC coupling in cardiac muscle:
1. An action potential enters a contractile cell, moves across the sarcolemma and into the t-tubules. It
opens voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ channels in the cell membrane.
2. Calcium entry into the cell through these channels causes the opening of RyR Ca2+ release channels
in the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
3. In this calcium-induced calcium release, stored calcium flows out of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and
into the cytosol, creating a Ca2+ “spark” that sums with other sparks from RyR channels to create the
Ca2+ signal
a. This provides roughly 90% of the calcium necessary
4. Contraction takes place by the same type of sliding filament movement that occurs in skeletal muscle
5. As cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentrations decrease, Ca2+ unbinds from troponin, myosin releases actin, and
the contractile filaments slide back to their relaxed position. As in skeletal muscle, Ca2+ is
transported back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum with the help of a Ca2+.ATPase. However, in cardiac
muscle, Ca2+ is also removed from the cell via the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger (NCX)
6. Sodium that enters the cell during this transfer is removed by the Na+-K+-ATPase