1. An expectant father tells the nurse he fears that his wife is "losing her mind." He states that she is
constantly rubbing her abdomen and talking to the baby and that she actually reprimands the baby
when it moves too much. Which recommendation should the nurse make to this expectant father?
A. Suggest that his wife seek professional counseling to deal with her symp- toms.
B. Explain that his wife is exhibiting ambivalence about the pregnancy.
C. Ask him to report similar abnormal behaviors at the next prenatal visit.
D. Reassure him that normal maternal-fetal bonding is occurring.
Answer> D) Reassure him that normal maternal-fetal bonding is occurring.
Rationale
These behaviors are positive signs of maternal-fetal bonding and do not reflect ambivalence. No
intervention is needed. Quickening, the first perception of fetal movement, occurs at 17 to 20 weeks of
gestation and begins a new phase of prenatal bonding during the second trimester. Options A and C are not
necessary because the behaviors displayed are normal.
2. The nurse is preparing a laboring client for an amniotomy. Immediately after the procedure is
completed, it is most important for the nurse to obtain which information?
A. Maternal blood pressure
B. Maternal temperature
,C. Fetal heart rate (FHR)
D. White blood cell count (WBC)
Answer> C. Fetal heart rate (FHR)
Rationale
The FHR should be assessed before and after the procedure to detect changes that may indicate the presence of
cord compression or prolapse. An amniotomy (artificial rupture of membranes [AROM]) is used to stimulate
labor when the condition of the cervix is favorable. The fluid should be assessed for color, odor, and
consistency.
Option A should be assessed every 15 to 20 minutes during labor but is not specific
for AROM. Option B is monitored hourly after the membranes are ruptured to detect the development of
amnionitis. Option D should be determined for all clients in labor.
3. A nurse receives a shift change report for a newborn who is 12 hours post-vaginal delivery.
In developing a plan of care, the nurse should give the highest priority to which finding?
A.Cyanosis of the hands and feet
B.Skin color that is slightly jaundiced C.Tiny white papules on the nose or chin
D.Red patches on the cheeks and trunk
Answer> B. Skin color that is slightly jaundiced
Rationale Jaundice, a yellow skin coloration, is caused by elevated levels of bilirubin, which should be further
evaluated in a newborn <24 hours old. Acrocyanosis (blue color of the hands and feet) is a common finding
in newborns; it occurs because the capillary system is immature. Milia are small white papules present on the
, nose and chin that are caused by sebaceous gland blockage and disappear in a few weeks. Small red patches
on the cheeks and trunk are called erythema toxicum neonatorum, a common finding in newborns.
4. A breastfeeding postpartum client is diagnosed with mastitis, and antibiotic therapy is
prescribed. Which instruction should the nurse provide to this client?
A. Breastfeed the infant, ensuring that both breasts are completely emptied.
B. Feed expressed breast milk to avoid the pain of the infant latching onto the infected breast.
C. Breastfeed on the unaffected breast only until the mastitis subsides.
D. Dilute expressed breast milk with sterile water to reduce the antibiotic effect on the infant.
Answer> A.Breastfeed the infant, ensuring that both breasts are completely emptied.
Rationale Mastitis, caused by plugged milk ducts, is related to breast engorgement, and breastfeeding during
mastitis facilitates the complete emptying of engorged breasts, eliminating the pressure on the inflamed
breast tissue. Option B is less
painful but does not facilitate complete emptying of the breast tissue. Option C will not relieve the
engorgement on the affected side. Option D will not decrease antibiotic effects on the infant.
5. A 38-week primigravida who works as a secretary and sits at a computer 8 hours each day tells
the nurse that her feet have begun to swell. Which instruc- tion will aid in the prevention of pooling of
blood in the lower extremities?
A. Wear support stockings.
, B. Reduce salt in the diet.
C. Move about every hour.
D. Avoid constrictive clothing.
Answer> C.Move about every hour.
Rationale
Pooling of blood in the lower extremities results from the enlarged uterus exerting pressure on the pelvic
veins. Moving about every hour will relieve pressure on the pelvic veins and increase venous return. Option A
would increase venous return from varicose veins in the lower extremities but would be of little help with
swelling. Option B might be helpful with generalized edema but is not specific for edematous lower
extremities. Option D does not address venous return, and there is no indication in the question that
constrictive clothing is a problem.
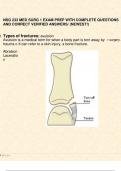
6. Twenty-four hours after admission to the newborn nursery, a full-term male infant develops
localized swelling on the right side of his head. In a newborn, what is the most likely cause of this
accumulation of blood between the periosteum and skull that does not cross the suture line?
A.Cephalhematoma, which is caused by forceps trauma B.Subarachnoid hematoma, which requires
immediate drainage C.Molding, which is caused by pressure during labor
D.Subdural hematoma, which can result in lifelong damage
Answer> A.Cephalhe- matoma, which is caused by forceps trauma
Rationale Cephalhematoma, a slight abnormal variation of the newborn, usually arises within the first 24
hours after delivery. Trauma from delivery causes capillary