🌟 Unit 2: Sensation and Perception
🔍 Key Concepts
Sensation: The physical process of detecting stimuli (e.g. light, sound, pressure) via
sensory organs.
Perception: The psychological process of interpreting and making sense of those stimuli.
The Five Senses
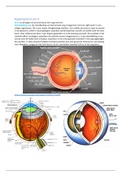
Vision: Uses light to detect shapes, colours, and movement via the eyes.
Hearing (Auditory): Detects sound waves via vibrations transmitted through the ear to the
brain.
Smell (Olfaction): Detects airborne molecules through receptors in the nose.
Taste (Gustation): Involves taste buds that identify sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami.
Touch (Somatosensation): Senses pressure, temperature, pain, and movement through
skin receptors.
Processing Types
Bottom-up processing: Builds perception from sensory input.
Top-down processing: Uses experience and knowledge to interpret sensory data.
, 👓 Perceptual Principles
Gestalt principles: Describe how we group elements (e.g. similarity, proximity, closure).
Sensory adaptation: The decline in sensitivity to a constant stimulus.
🌊 Waves and Perception
Amplitude: Height of a wave; affects brightness (vision) or loudness (hearing).
Wavelength: Distance between wave peaks; affects colour (vision) or pitch (hearing).
Unit 3: Cognition – Thinking, Reasoning, and Problem-Solving
What Is Cognition?
Mental processes related to thinking, understanding, reasoning, and communication.
Mental Representations
Mental images – Picture-like representations in the mind.
Concepts – Categories for grouping information.
Formal concepts: Strict rules (e.g. square).
Natural concepts: Everyday, “fuzzy” categories (e.g. bird).
Prototypes – Best examples of a concept.
🔍 Key Concepts
Sensation: The physical process of detecting stimuli (e.g. light, sound, pressure) via
sensory organs.
Perception: The psychological process of interpreting and making sense of those stimuli.
The Five Senses
Vision: Uses light to detect shapes, colours, and movement via the eyes.
Hearing (Auditory): Detects sound waves via vibrations transmitted through the ear to the
brain.
Smell (Olfaction): Detects airborne molecules through receptors in the nose.
Taste (Gustation): Involves taste buds that identify sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami.
Touch (Somatosensation): Senses pressure, temperature, pain, and movement through
skin receptors.
Processing Types
Bottom-up processing: Builds perception from sensory input.
Top-down processing: Uses experience and knowledge to interpret sensory data.
, 👓 Perceptual Principles
Gestalt principles: Describe how we group elements (e.g. similarity, proximity, closure).
Sensory adaptation: The decline in sensitivity to a constant stimulus.
🌊 Waves and Perception
Amplitude: Height of a wave; affects brightness (vision) or loudness (hearing).
Wavelength: Distance between wave peaks; affects colour (vision) or pitch (hearing).
Unit 3: Cognition – Thinking, Reasoning, and Problem-Solving
What Is Cognition?
Mental processes related to thinking, understanding, reasoning, and communication.
Mental Representations
Mental images – Picture-like representations in the mind.
Concepts – Categories for grouping information.
Formal concepts: Strict rules (e.g. square).
Natural concepts: Everyday, “fuzzy” categories (e.g. bird).
Prototypes – Best examples of a concept.