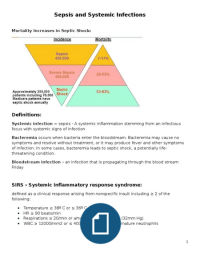
with correct answers respectively.
Biological Psychology ANS - A branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and
behavior. (Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists)
Neuron ANS - A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Sensory Neurons ANS - Neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the
brain and spinal cord
Motor Neurons ANS - Neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the
muscles and gland
Interneurons ANS - Neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene
between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
Dendrite ANS - The bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct
impulses toward the cell body
Axon ANS - The extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages
pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
Myelin sheath ANS - A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables
vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next
Action potential ANS - A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Threshold ANS - The level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
This study source was downloaded by 100000899568844 from CourseHero.com on 06-11-2025 16:47:27 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/247002579/College-Psychology-Chapter-2-questions-with-correct-answers-respectivelydocx/
, Synapse ANS - The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of
the receiving neuron. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitters ANS - Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When
released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites
on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse
Reuptake ANS - A neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
Endorphins ANS - "Morphine within" - natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and
to pleasure
Nervous System ANS - The body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the
nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous system
Central Nervous System ANS - (CNS) the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System ANS - (PNS) the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central
nervous system to the rest of the body
Nerves ANS - Bundled axons that form neural "cables" connecting the central nervous system with
muscles, glands, and sense organs
Somatic Nervous System ANS - The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's
skeletal muscles. Called the skeletal nervous system
Autonomic Nervous System ANS - The part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands
and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its
parasympathetic division calms
Sympathetic Nervous System ANS - The division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the
body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
This study source was downloaded by 100000899568844 from CourseHero.com on 06-11-2025 16:47:27 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/247002579/College-Psychology-Chapter-2-questions-with-correct-answers-respectivelydocx/