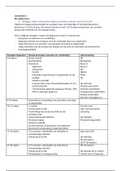
Chapter 1
There are 3 types of Flows:
1. Flow of Materials: goods flow from the supplier’s supplier through to the end customer.
2. Flow of Information: order confirmation or dispatch advice.
3. Reverse Flows (flows for funds): goods, information, packaging material, transporting
equipment. Money that flows back into the supply chain.
Supply chain forces
1. Customer Demand: customer starts the chain of supply, manufacturing and transport
activities of your desired product. customer demand is when the supply chain after the
order
2. Product Supply (commodities): the supply chain starts supplying before there is a
customer demand for it. Product supply (primary goods) is already there (supply chain
has already taken place) or the products are sourced, produced and shipped in advance
A Functional View of Supply Chain Management:
Supply Chain Operating Reference model (SCOR)
,5 main functional processes
1. Plan process:
- Demand and supply are balanced to develop a course of action. (ERP Systems)
- The plan process aligns the supply chain with the financial plan
2. Source Process:
- selecting suppliers,
- establishing policies and assessing performance. Once supply and demand are
sourced you can start the making process.
- describes the process of buying goods or services to meet planned or actual
demand
3. Make Process:
- transforming the raw material into the finished product with the aim to meet the
demand. Set up, scheduling of the manufacturing.
4. Delivery Process:
- order management, warehousing and logistics (transportation)
- all processes that transform your raw materials or sub-assemblies into the finished
product with the aim to meet customer demand
5. Return Process:
- post-delivery customer support.
- This functional process comprises all tasks that are associated with the return of
product. Returns can occur for quality reasons, for recycling or for post delivery
customer support
Supply Chain Players:
Supplier
Company
Customer
Service Provider (transport, warehouse etc.)
- Extended supply chain includes an upstream side (towards the supply) and a
downstream side (towards the demand).
*remember that customers do not have be always the end customers
Flow upstream: supplier
Flow downstream: customer
,Extended supply chain includes an upstream side (towards the supply) and a downstream side
(towards the demand).
*remember that customers do not have be always the end customers
Supply chains react to changes in their environment
- Customer demand
- Product supply
- Exchange rates
- Temperature
Managing inventory levels
- The higher the inventory level the higher the customer service
- The lower the inventory the more efficient
, Chapter 3
Sourcing is one the components of the supply chain operations reference model, it is the
interference between the suppliers and the buying company.
Effective sourcing benefits
• Improved quality (improving the quality of raw materials and finally the final product) –
customers are happy
• Development of product technology
• Cash flow improvement (delay payment, thus more money in the company)
• Cost reduction
• Reduced cycle times
Sourcing: in product companies generally involves dividing products or services into two distinct
groups: direct and indirect items
1. Direct items- are directly related to the products manufacturing process. ( a part of
the final product ) eg. Raw materials
2. Indirect items- describe all the other products and services that are needed to run the
company. (not physically present on the product ) eg. Electricity
The Purchasing Process: (purchase-to-pay process) it can be divided into two parts- the pre-
order process and the post-order process.
Pre-order steps:
Need Specification Sourcing
Selection Negotiation Tendering
Contracts
There are 3 types of Flows:
1. Flow of Materials: goods flow from the supplier’s supplier through to the end customer.
2. Flow of Information: order confirmation or dispatch advice.
3. Reverse Flows (flows for funds): goods, information, packaging material, transporting
equipment. Money that flows back into the supply chain.
Supply chain forces
1. Customer Demand: customer starts the chain of supply, manufacturing and transport
activities of your desired product. customer demand is when the supply chain after the
order
2. Product Supply (commodities): the supply chain starts supplying before there is a
customer demand for it. Product supply (primary goods) is already there (supply chain
has already taken place) or the products are sourced, produced and shipped in advance
A Functional View of Supply Chain Management:
Supply Chain Operating Reference model (SCOR)
,5 main functional processes
1. Plan process:
- Demand and supply are balanced to develop a course of action. (ERP Systems)
- The plan process aligns the supply chain with the financial plan
2. Source Process:
- selecting suppliers,
- establishing policies and assessing performance. Once supply and demand are
sourced you can start the making process.
- describes the process of buying goods or services to meet planned or actual
demand
3. Make Process:
- transforming the raw material into the finished product with the aim to meet the
demand. Set up, scheduling of the manufacturing.
4. Delivery Process:
- order management, warehousing and logistics (transportation)
- all processes that transform your raw materials or sub-assemblies into the finished
product with the aim to meet customer demand
5. Return Process:
- post-delivery customer support.
- This functional process comprises all tasks that are associated with the return of
product. Returns can occur for quality reasons, for recycling or for post delivery
customer support
Supply Chain Players:
Supplier
Company
Customer
Service Provider (transport, warehouse etc.)
- Extended supply chain includes an upstream side (towards the supply) and a
downstream side (towards the demand).
*remember that customers do not have be always the end customers
Flow upstream: supplier
Flow downstream: customer
,Extended supply chain includes an upstream side (towards the supply) and a downstream side
(towards the demand).
*remember that customers do not have be always the end customers
Supply chains react to changes in their environment
- Customer demand
- Product supply
- Exchange rates
- Temperature
Managing inventory levels
- The higher the inventory level the higher the customer service
- The lower the inventory the more efficient
, Chapter 3
Sourcing is one the components of the supply chain operations reference model, it is the
interference between the suppliers and the buying company.
Effective sourcing benefits
• Improved quality (improving the quality of raw materials and finally the final product) –
customers are happy
• Development of product technology
• Cash flow improvement (delay payment, thus more money in the company)
• Cost reduction
• Reduced cycle times
Sourcing: in product companies generally involves dividing products or services into two distinct
groups: direct and indirect items
1. Direct items- are directly related to the products manufacturing process. ( a part of
the final product ) eg. Raw materials
2. Indirect items- describe all the other products and services that are needed to run the
company. (not physically present on the product ) eg. Electricity
The Purchasing Process: (purchase-to-pay process) it can be divided into two parts- the pre-
order process and the post-order process.
Pre-order steps:
Need Specification Sourcing
Selection Negotiation Tendering
Contracts