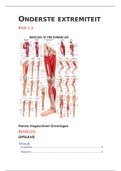
Kolb : chapter 24
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
● Physical Symptoms: irregular facial features (smooth philtrum, thin upper lip and short
palpebral fissures), brain irregularities (small brains with abnormal gyri, normal sized
brains with clusters of cells and misaligned cells in the cortex), small stature, thin
● Behavioral symptoms : learning disability, lowered intelligence scores, hyperactivity,
social problems
● Found in 6% offspring of alcoholic mothers
● High incidence in child-care settings and among prison populations
● Severity related to amount/timing/frequency of alcohol consumption + individual factors
● Worst effects in first 3 months of pregnancy (sensitive period hypothesis)
● Severe FASD more likely to be caused by binge drinking
● Poor maternal nutrition and using other drugs and nicotine also factors
● findings that as little as one alcoholic drink per day during pregnancy can lead to
decreased intelligence test scores in offspring findings that as little as one alcoholic drink
per day during pregnancy can lead to decreased intelligence test scores in offspring
● In males alcohol may produce epigenetic changes in sperm that affects fetal
development
● Pregnant woman should completely avoid alcohol
● Alcohol has an inhibitory effect on Kir 2.1 channels (allow K+ to move freely across cell
membrane, which is important for maintaining a normal resting potential)
○ When Kir 2.1 channel is blocked → apoptosis
○ Apoptosis can cause brain abnormalities in FASD
Kolb : chapter 26
Multiple sclerosis
● Disorder of myelinated motor fibers, characterized by a loss of myelin, largely in motor
tracts but also in sensory tracts
● Myelin loss is not uniform, but lost in patches → small, hard, circumscribed scars →
sclerotic plaques, in which the myelin sheath and sometimes the axons are destroyed
● MS symptoms : loss of sensation in the face, limbs, body; blurring of vision, loss of
sensation and control in one or more limbs
, ● Often early symptoms go into remission and do not appear again for years
● In some people the disease progresses rapidly
● Cause of MS unknown, but has genetic component
● 50 per 100,000 people suffer
● F:M 3:2, progress often more rapid in females than males
● Prevalence of MS at northern latitudes → vitamin D deficiency?
○ Vitamin D may be important for myelin development in childhood and for
maintenance in adulthood
● alemtuzumab (Lemtrada), which destroys a class of immune cells that attack healthy
body tissue, shows promise for treating MS
● brain–computer interface (BCI) technology likewise hold promise for aiding mobility in
people with rapidly progressing multiple sclerosis
Kolb : chapter 27
Motor disorders
Hyperkinetic disorders
Huntington’s disease
● Intellectual deterioration and personality changes and abnormal movements = choreas
● First symptoms appear 30-50 years
● The first involuntary movements usually appear within a year of the onset of the
behavioral symptoms
○ Initially slight and consist of little more than continual fidgeting but slowly increase
until they are almost incessant and irregular
● Behavioral symptoms : impairment of recent memory, defective ability to manipulate
acquired knowledge, slow information processing
● Emotional changes : anxiety, depression, mania, schizophrenia like psychosis
● Patients live on average 12 years after onset
● Transmitted genetically as an autosomal dominant allele with complete penetrance →
half of the offspring will develop the disease
● Brain autopsy findings : cortical shrinkage and thinning, basal ganglia grossly atrophied
and neuronal loss
● Dominant explanation : imbalance among the various neurotransmitter systems of the
basal ganglia
1. A glutamate projection from cortex to basal ganglia
2. A GABA projection from the basal ganglia to the substantia nigra, a nucleus in the
midbrain involved in initiating movement
3. A dopamine projection from the substantia nigra to the basal ganglia
4. Acetylcholine ACh neurons in the basal ganglia
● Intrinsic neurons of the basal ganglia die in the curse of the disease, leaving a largely
intact nigrostriatal dopamine pathway
,● Decreased inhibition of dopamine by GABA → increased dopamine in basal ganglia →
choreas
● Patients are especially bad at various frontal lobe test (can be used as predictors)
, Tourette’s syndrome
● Three stages of symptoms
○ First stage : multiple tics
○ Second stage : inarticulate cries accompany the multiple tics
○ Third stage : emission of articulate words with echolalia ( repeating what others
have said as well as repeating actions) and coprolalia (obscene speech)
● People with the symptom can be intelligent and productive
● Hereditary
● No treatment
● 1 in 360 people, onset around 7 y/o
● Most frequent symptoms : tics of the eye, head or face, upper limbs and lower limbs and
body
● Complex movements including touching, hitting and jumping occur in some cases
● Abnormalities occur in frontoparietal circuitry
● Most improvements are obtained with antidopaminergic agents (haloperidol) →
abnormality in basal ganglia
● Norepinephrine-receptor agonists also work in some cases
● Abnormalities in some cognitive functions usually supported by the right hemisphere
○ Kids with TS were especially bad at drawing and remembering complex
geometric figures
Hypokinetic disorders
Parkinson’s disease
● 0.1-1% of the population
● Four major symptoms
○ Tremor
○ Muscular rigidity
○ Involuntary movements
○ Postural disturbance
● Symptoms reflecting acquisitions of abnormal behaviors → positive symptoms
● Symptoms reflecting loss of normal behaviors → negative symptoms
Positive symptoms
1. Tremor at rest → alternating movements of the limbs when they are at rest stop during
voluntary movements or during sleep
2. Muscular rigidity → increased muscle tone in extensor and flexor muscles, movement
is resisted but with sufficient force the muscles yield for a short distance and then resist
movement again → cogwheel rigidity
3. involuntary movements → akathisia/cruel restlessness may be concurrent with
general inactivity
a. Oculogyric crisis - involuntary turns of the head and eyes to one side
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
● Physical Symptoms: irregular facial features (smooth philtrum, thin upper lip and short
palpebral fissures), brain irregularities (small brains with abnormal gyri, normal sized
brains with clusters of cells and misaligned cells in the cortex), small stature, thin
● Behavioral symptoms : learning disability, lowered intelligence scores, hyperactivity,
social problems
● Found in 6% offspring of alcoholic mothers
● High incidence in child-care settings and among prison populations
● Severity related to amount/timing/frequency of alcohol consumption + individual factors
● Worst effects in first 3 months of pregnancy (sensitive period hypothesis)
● Severe FASD more likely to be caused by binge drinking
● Poor maternal nutrition and using other drugs and nicotine also factors
● findings that as little as one alcoholic drink per day during pregnancy can lead to
decreased intelligence test scores in offspring findings that as little as one alcoholic drink
per day during pregnancy can lead to decreased intelligence test scores in offspring
● In males alcohol may produce epigenetic changes in sperm that affects fetal
development
● Pregnant woman should completely avoid alcohol
● Alcohol has an inhibitory effect on Kir 2.1 channels (allow K+ to move freely across cell
membrane, which is important for maintaining a normal resting potential)
○ When Kir 2.1 channel is blocked → apoptosis
○ Apoptosis can cause brain abnormalities in FASD
Kolb : chapter 26
Multiple sclerosis
● Disorder of myelinated motor fibers, characterized by a loss of myelin, largely in motor
tracts but also in sensory tracts
● Myelin loss is not uniform, but lost in patches → small, hard, circumscribed scars →
sclerotic plaques, in which the myelin sheath and sometimes the axons are destroyed
● MS symptoms : loss of sensation in the face, limbs, body; blurring of vision, loss of
sensation and control in one or more limbs
, ● Often early symptoms go into remission and do not appear again for years
● In some people the disease progresses rapidly
● Cause of MS unknown, but has genetic component
● 50 per 100,000 people suffer
● F:M 3:2, progress often more rapid in females than males
● Prevalence of MS at northern latitudes → vitamin D deficiency?
○ Vitamin D may be important for myelin development in childhood and for
maintenance in adulthood
● alemtuzumab (Lemtrada), which destroys a class of immune cells that attack healthy
body tissue, shows promise for treating MS
● brain–computer interface (BCI) technology likewise hold promise for aiding mobility in
people with rapidly progressing multiple sclerosis
Kolb : chapter 27
Motor disorders
Hyperkinetic disorders
Huntington’s disease
● Intellectual deterioration and personality changes and abnormal movements = choreas
● First symptoms appear 30-50 years
● The first involuntary movements usually appear within a year of the onset of the
behavioral symptoms
○ Initially slight and consist of little more than continual fidgeting but slowly increase
until they are almost incessant and irregular
● Behavioral symptoms : impairment of recent memory, defective ability to manipulate
acquired knowledge, slow information processing
● Emotional changes : anxiety, depression, mania, schizophrenia like psychosis
● Patients live on average 12 years after onset
● Transmitted genetically as an autosomal dominant allele with complete penetrance →
half of the offspring will develop the disease
● Brain autopsy findings : cortical shrinkage and thinning, basal ganglia grossly atrophied
and neuronal loss
● Dominant explanation : imbalance among the various neurotransmitter systems of the
basal ganglia
1. A glutamate projection from cortex to basal ganglia
2. A GABA projection from the basal ganglia to the substantia nigra, a nucleus in the
midbrain involved in initiating movement
3. A dopamine projection from the substantia nigra to the basal ganglia
4. Acetylcholine ACh neurons in the basal ganglia
● Intrinsic neurons of the basal ganglia die in the curse of the disease, leaving a largely
intact nigrostriatal dopamine pathway
,● Decreased inhibition of dopamine by GABA → increased dopamine in basal ganglia →
choreas
● Patients are especially bad at various frontal lobe test (can be used as predictors)
, Tourette’s syndrome
● Three stages of symptoms
○ First stage : multiple tics
○ Second stage : inarticulate cries accompany the multiple tics
○ Third stage : emission of articulate words with echolalia ( repeating what others
have said as well as repeating actions) and coprolalia (obscene speech)
● People with the symptom can be intelligent and productive
● Hereditary
● No treatment
● 1 in 360 people, onset around 7 y/o
● Most frequent symptoms : tics of the eye, head or face, upper limbs and lower limbs and
body
● Complex movements including touching, hitting and jumping occur in some cases
● Abnormalities occur in frontoparietal circuitry
● Most improvements are obtained with antidopaminergic agents (haloperidol) →
abnormality in basal ganglia
● Norepinephrine-receptor agonists also work in some cases
● Abnormalities in some cognitive functions usually supported by the right hemisphere
○ Kids with TS were especially bad at drawing and remembering complex
geometric figures
Hypokinetic disorders
Parkinson’s disease
● 0.1-1% of the population
● Four major symptoms
○ Tremor
○ Muscular rigidity
○ Involuntary movements
○ Postural disturbance
● Symptoms reflecting acquisitions of abnormal behaviors → positive symptoms
● Symptoms reflecting loss of normal behaviors → negative symptoms
Positive symptoms
1. Tremor at rest → alternating movements of the limbs when they are at rest stop during
voluntary movements or during sleep
2. Muscular rigidity → increased muscle tone in extensor and flexor muscles, movement
is resisted but with sufficient force the muscles yield for a short distance and then resist
movement again → cogwheel rigidity
3. involuntary movements → akathisia/cruel restlessness may be concurrent with
general inactivity
a. Oculogyric crisis - involuntary turns of the head and eyes to one side