Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Exam
Questions and Answers
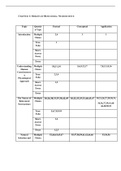
Metabolism
The sum of all the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Catabolism
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules, releasing energy.
Anabolism
Metabolic pathways that construct molecules, requiring energy.
Cellular Respiration Equation
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP energy
Enzyme
A protein that acts as a biological catalyst to speed up a chemical reaction
Enzyme-substrate complex
When an enzyme binds to its substrate
Active Site
A region on an enzyme that binds to a substrate during a reaction.
Lock and Key Theory
,Enzyme's active site (lock) is already in appropriate conformation for the
substrate (key) to bind
Substrate easily fits into active site
Glycolosis
Breaking glucose into two molecules of a compound called pyruvate; Creates a
net total of 2 ATPs; anaerobic; occurs in cytosol
Krebs Cycle
second stage of cellular respiration; occurs in mitochondria; pyruvate molecules
are turned into ATPs;Generates 2 ATPs; aerobic
Electron Transport Chain
Uses the high-energy electrons from the Krebs cycle to convert ADP into ATP;
aerobic; Generates 34 ATPs
Epithilial tissue
Tissue composed of layers of closely spaced cells that cover organ surfaces; e.g.
skin
Connective Tissue
A tissue that provides support for the body and connects its parts; e.g. blood,
cartilage
Muscular Tissue
Long thin tissue that contracts to create movement; e.g. cardiac muscle, skeletal
muscle
Nervous Tissue
Tissue that carries info between the brain and other parts of the body; e.g.
neurones
,Lungs
Two organs, located in the thoracic cavity responsible for breathing
Nasal Cavity
hollow space behind the nose; filters and warms air
Pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
Larynx
passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
Pleural Membrane
membrane that encloses the lungs within the rib cage
, Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering.
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs
Ribs
The bones in the chest that protect the heart and lungs.
Bronchi
The passages that direct air into the lungs
Intercostal Muscles
Muscles which move the rib cage during breathing
Cell Membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
Alveoli
small sacs within the lungs where gas exchange takes place with the bloodstream
Gas Exchange
Questions and Answers
Metabolism
The sum of all the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Catabolism
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules, releasing energy.
Anabolism
Metabolic pathways that construct molecules, requiring energy.
Cellular Respiration Equation
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP energy
Enzyme
A protein that acts as a biological catalyst to speed up a chemical reaction
Enzyme-substrate complex
When an enzyme binds to its substrate
Active Site
A region on an enzyme that binds to a substrate during a reaction.
Lock and Key Theory
,Enzyme's active site (lock) is already in appropriate conformation for the
substrate (key) to bind
Substrate easily fits into active site
Glycolosis
Breaking glucose into two molecules of a compound called pyruvate; Creates a
net total of 2 ATPs; anaerobic; occurs in cytosol
Krebs Cycle
second stage of cellular respiration; occurs in mitochondria; pyruvate molecules
are turned into ATPs;Generates 2 ATPs; aerobic
Electron Transport Chain
Uses the high-energy electrons from the Krebs cycle to convert ADP into ATP;
aerobic; Generates 34 ATPs
Epithilial tissue
Tissue composed of layers of closely spaced cells that cover organ surfaces; e.g.
skin
Connective Tissue
A tissue that provides support for the body and connects its parts; e.g. blood,
cartilage
Muscular Tissue
Long thin tissue that contracts to create movement; e.g. cardiac muscle, skeletal
muscle
Nervous Tissue
Tissue that carries info between the brain and other parts of the body; e.g.
neurones
,Lungs
Two organs, located in the thoracic cavity responsible for breathing
Nasal Cavity
hollow space behind the nose; filters and warms air
Pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
Larynx
passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
Pleural Membrane
membrane that encloses the lungs within the rib cage
, Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering.
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs
Ribs
The bones in the chest that protect the heart and lungs.
Bronchi
The passages that direct air into the lungs
Intercostal Muscles
Muscles which move the rib cage during breathing
Cell Membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
Alveoli
small sacs within the lungs where gas exchange takes place with the bloodstream
Gas Exchange