MEDICAL CODING AND BILLING CERTIFICATION (mcbc) EXAM
LATEST 2025 WITH CORRECT QUESTIONS AND DETAILED
ANSWERS/ALREADY GRADED A+
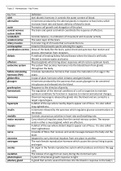
Chief Complaint (element 1 of history) - CORRECT ANSWER-History of present
illness,
Review symptom,
Past, Family, and Social history
History Levels (Element 2 of history) and Examination Levels (Element 3 of
History) - CORRECT ANSWER-Problem focused,
expanded problem focused,
detailed,
Comprehensive
Medical Decision Making Complexity Levels (element 4 of history) - CORRECT
ANSWER-Straightforward,
Low,
Moderate,
,High
straightforward - CORRECT ANSWER-Minimal diagnosis
Minimal risk
Minimal complexity of data
Low - CORRECT ANSWER-Limited diagnosis
Limited/low risk to patient
Limited data
Moderate - CORRECT ANSWER-Multiple diagnosis
Moderate risk to patient
Moderate amount and complexity of data
high - CORRECT ANSWER-Extensive diagnosis
high risk to patient
extensive amount and complexity of data
truncated coding (error in coding) - CORRECT ANSWER-using diagnosis codes
that are not as specific as possible
,assumption coding (fraudulent coding) - CORRECT ANSWER-reporting items of
services that are not actually documented
errors of the coding process - CORRECT ANSWER--altering documentation after
services are reported
-coding without documentation
-reporting services provided by unlicensed or unqualified clinical personnel
-coding a unilateral service twice instead of choosing the bilateral
-not satisfying the condition of coverage for a particular service
-codes that report more than one diagnosis with one code is a combination code
Unbundling codes - CORRECT ANSWER-when multiple codes are used to code a
procedure when a single code should be used
Upcoding - CORRECT ANSWER-using a procedural code that provides a higher
reimbursement rate than the correct code
Downcoding - CORRECT ANSWER-the document does not justify the level of
service
Most common billing errors - CORRECT ANSWER-Billing non-covered services
Billing over limit services
Upcoding
, Downcoding
Billing without signatures
Using outdated codes
External Audits
Internal Audits
Retrospective audits - CORRECT ANSWER-Types of Audits done to avoid billing
and coding errors
External Audits - CORRECT ANSWER-a private payer or government
investigator's review of selected records of a practice for compliance
Internal Audits - CORRECT ANSWER-self-audit conducted by a staff member or
consultant
Retrospective Audits - CORRECT ANSWER-conducted after the claim has been
send the remittance advice has been received
Adjustments - CORRECT ANSWER-amounts added to or taken away from the
balance of an account
Two methods to determine rates to be paid to providers - CORRECT ANSWER-
Charge; Resource
LATEST 2025 WITH CORRECT QUESTIONS AND DETAILED
ANSWERS/ALREADY GRADED A+
Chief Complaint (element 1 of history) - CORRECT ANSWER-History of present
illness,
Review symptom,
Past, Family, and Social history
History Levels (Element 2 of history) and Examination Levels (Element 3 of
History) - CORRECT ANSWER-Problem focused,
expanded problem focused,
detailed,
Comprehensive
Medical Decision Making Complexity Levels (element 4 of history) - CORRECT
ANSWER-Straightforward,
Low,
Moderate,
,High
straightforward - CORRECT ANSWER-Minimal diagnosis
Minimal risk
Minimal complexity of data
Low - CORRECT ANSWER-Limited diagnosis
Limited/low risk to patient
Limited data
Moderate - CORRECT ANSWER-Multiple diagnosis
Moderate risk to patient
Moderate amount and complexity of data
high - CORRECT ANSWER-Extensive diagnosis
high risk to patient
extensive amount and complexity of data
truncated coding (error in coding) - CORRECT ANSWER-using diagnosis codes
that are not as specific as possible
,assumption coding (fraudulent coding) - CORRECT ANSWER-reporting items of
services that are not actually documented
errors of the coding process - CORRECT ANSWER--altering documentation after
services are reported
-coding without documentation
-reporting services provided by unlicensed or unqualified clinical personnel
-coding a unilateral service twice instead of choosing the bilateral
-not satisfying the condition of coverage for a particular service
-codes that report more than one diagnosis with one code is a combination code
Unbundling codes - CORRECT ANSWER-when multiple codes are used to code a
procedure when a single code should be used
Upcoding - CORRECT ANSWER-using a procedural code that provides a higher
reimbursement rate than the correct code
Downcoding - CORRECT ANSWER-the document does not justify the level of
service
Most common billing errors - CORRECT ANSWER-Billing non-covered services
Billing over limit services
Upcoding
, Downcoding
Billing without signatures
Using outdated codes
External Audits
Internal Audits
Retrospective audits - CORRECT ANSWER-Types of Audits done to avoid billing
and coding errors
External Audits - CORRECT ANSWER-a private payer or government
investigator's review of selected records of a practice for compliance
Internal Audits - CORRECT ANSWER-self-audit conducted by a staff member or
consultant
Retrospective Audits - CORRECT ANSWER-conducted after the claim has been
send the remittance advice has been received
Adjustments - CORRECT ANSWER-amounts added to or taken away from the
balance of an account
Two methods to determine rates to be paid to providers - CORRECT ANSWER-
Charge; Resource