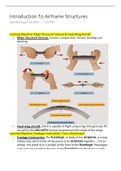
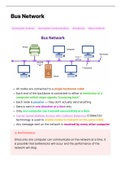
Batch Operating System
Introduction:
A Batch Operating System is a type of operating system in which tasks or jobs are
executed in batches without user interaction. Unlike interactive operating
systems (like Windows or macOS), a batch operating system executes a series of
programs or jobs one after another in a sequential manner. Users submit their
jobs in batches, and the operating system schedules them for execution. Once the
batch job is completed, the user can view the output.
Batch operating systems were primarily used in early computer systems when
interactive computing was not yet feasible. They are typically employed for tasks
that do not require user interaction, such as processing large volumes of data,
scientific calculations, and administrative tasks.
Key Characteristics of Batch Operating Systems:
1. Job Pooling:
o In a batch operating system, users submit their jobs in job pools or
queues. These jobs are collected and processed in batches, meaning
the system processes a group of jobs together without interruption.
o Jobs are usually similar in nature (e.g., similar types of calculations or
data processing tasks), making batch processing more efficient.
2. Sequential Execution:
o Batch systems are designed to execute jobs sequentially, one after
the other, based on their priority or order of arrival. There is no
direct user interaction during the execution phase, and the system
automatically manages the sequence in which jobs are executed.
o This sequential execution helps maximize the use of system
resources, as the CPU can focus entirely on executing the next task
without waiting for user input.
3. Job Scheduling:
o Job scheduling is an important function in a batch operating system.
The scheduler organizes the jobs in a queue, determining the order in
which they are executed based on factors like priority, resource
availability, and dependencies.
, o The system typically uses predefined scheduling algorithms, such as
First-Come, First-Served (FCFS) or Shortest Job Next (SJN), to
process jobs efficiently.
4. No Direct User Interaction:
o In a batch operating system, the user does not interact directly with
the system while jobs are running. Instead, the user prepares a batch
of tasks or jobs, which are submitted to the system for execution.
Once the job completes, the user receives the results, usually in the
form of printed reports or file outputs.
o This lack of direct interaction can be both a strength and a limitation,
as users must prepare their jobs ahead of time and cannot make
changes or corrections during the execution process.
5. Limited Input/Output Processing:
o In batch systems, input and output (I/O) operations are typically
handled before and after the execution of a job. Since jobs run
without user interaction, the system processes the input data, runs
the necessary tasks, and then generates output once the job is
complete.
o Input and output operations are often batched as well, with files
being read in bulk and written out as a single result.
6. Resource Management:
o Batch operating systems efficiently allocate system resources (CPU
time, memory, and I/O devices) to different jobs. Since there is no
user intervention during job execution, the system can manage
resources without interruption.
o The operating system may implement mechanisms like
multiprogramming to ensure that while one job is waiting for I/O
operations, another job can be processed, thus maximizing CPU
utilization.
Advantages of Batch Operating Systems:
1. Efficient Processing:
o By grouping similar jobs together and executing them sequentially,
batch operating systems can optimize system resources, such as CPU
and memory, ensuring maximum efficiency.
Introduction:
A Batch Operating System is a type of operating system in which tasks or jobs are
executed in batches without user interaction. Unlike interactive operating
systems (like Windows or macOS), a batch operating system executes a series of
programs or jobs one after another in a sequential manner. Users submit their
jobs in batches, and the operating system schedules them for execution. Once the
batch job is completed, the user can view the output.
Batch operating systems were primarily used in early computer systems when
interactive computing was not yet feasible. They are typically employed for tasks
that do not require user interaction, such as processing large volumes of data,
scientific calculations, and administrative tasks.
Key Characteristics of Batch Operating Systems:
1. Job Pooling:
o In a batch operating system, users submit their jobs in job pools or
queues. These jobs are collected and processed in batches, meaning
the system processes a group of jobs together without interruption.
o Jobs are usually similar in nature (e.g., similar types of calculations or
data processing tasks), making batch processing more efficient.
2. Sequential Execution:
o Batch systems are designed to execute jobs sequentially, one after
the other, based on their priority or order of arrival. There is no
direct user interaction during the execution phase, and the system
automatically manages the sequence in which jobs are executed.
o This sequential execution helps maximize the use of system
resources, as the CPU can focus entirely on executing the next task
without waiting for user input.
3. Job Scheduling:
o Job scheduling is an important function in a batch operating system.
The scheduler organizes the jobs in a queue, determining the order in
which they are executed based on factors like priority, resource
availability, and dependencies.
, o The system typically uses predefined scheduling algorithms, such as
First-Come, First-Served (FCFS) or Shortest Job Next (SJN), to
process jobs efficiently.
4. No Direct User Interaction:
o In a batch operating system, the user does not interact directly with
the system while jobs are running. Instead, the user prepares a batch
of tasks or jobs, which are submitted to the system for execution.
Once the job completes, the user receives the results, usually in the
form of printed reports or file outputs.
o This lack of direct interaction can be both a strength and a limitation,
as users must prepare their jobs ahead of time and cannot make
changes or corrections during the execution process.
5. Limited Input/Output Processing:
o In batch systems, input and output (I/O) operations are typically
handled before and after the execution of a job. Since jobs run
without user interaction, the system processes the input data, runs
the necessary tasks, and then generates output once the job is
complete.
o Input and output operations are often batched as well, with files
being read in bulk and written out as a single result.
6. Resource Management:
o Batch operating systems efficiently allocate system resources (CPU
time, memory, and I/O devices) to different jobs. Since there is no
user intervention during job execution, the system can manage
resources without interruption.
o The operating system may implement mechanisms like
multiprogramming to ensure that while one job is waiting for I/O
operations, another job can be processed, thus maximizing CPU
utilization.
Advantages of Batch Operating Systems:
1. Efficient Processing:
o By grouping similar jobs together and executing them sequentially,
batch operating systems can optimize system resources, such as CPU
and memory, ensuring maximum efficiency.