Transport economics
1 The traffic and transport system
Derived demand
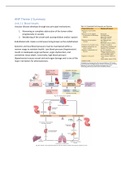
➔ Let us assume that a particular commodity is supplied at Antwerp (Sa) and is demanded in
Ghent (Dg). For a given quantity X the supplier is prepared to deliver the commodity at a price
OB. The buyer for his part, in accordance with the utility that he assigns to the product, is
willing to pay OC. The difference between the demand price and the supply price of the product
(OC – OB) provides the basis for calculating the costs of transportation. The difference
between the price at place of origin and the price at the destination determines the maximum
price the buyer is willing to pay to have the product transported form Antwerp to Ghent. If
transportation cost is greater than this difference, the he will no longer be willing to buy the
product. By confronting de demand and supply curves, we can derive the demand for
transportation (Dt). At a given quantity X, there is a willingness to pay a maximum price OT (=
OC – OB) for transportation. At a quantity Y, where the demand and supply curves for the
product intersect each other, there is no longer any price difference to serve as a basis for the
price of transportation. The demand curve for transportation (Dt) will intersect the X-axis in this
point.
,1.1 Preliminaries
➔ Traffic and transportation hardly ever arise spontaneously
➔ Traffic and transportation are the result of some other primary need for goods and services
➔ Traffic and transportation thus shows an intermediary character and it is a derived need
(derived nature)
➔ Graphical analysis : the derived nature of transport demand
- Starting situation: a commodity is supplied in Antwerp and demanded for in Ghent, and the
commodity thus needs to be transported
- Step 1: consider a quantity x (less than Y)
- Step 2: determine the delivery price OB
- Step 3: determine the willingness to pay OC
- Step 4: OC – OB gives the basics of calculating the MAXIMUM cost of transportation
- Step 5: derive Dt
- Step 6: assume St (upward sloping curve and based on marginal costs)
- Step 7: determine E (new quantity equilibrium taking into account transportation costs)
1.2 The traffic and transportation system
1.2.1 The difference between traffic and transportation
➔ Traffic consists of 2 components
- a) Means of transport: mobile capital goods like vehicles, trains, vessels, aeroplanes, etc.
- (b) Infrastructure: fixed capital goods
- (a) and (b) are PERMANENT COMPONENTS and result into a so-called traffic
performance
➔ Transportation takes into account the two permanent components of traffic plus the variable
component load
➔ Transportation thus exists of
- (a) Means of transport
- (b) Infrastructure
- (c) Load
1.2.2 Transportation subsystems
1.2.2.1 Classification by type of load
Passenger transport
Individual Common (gemeenschappelijk)
Private Car, bicycle, motorbike School buses, coach, services
Public Taxi Train, tram, bus, underground, plains
➔ Public transport : government-imposed regulations
, Freight transport
➔ Bulk cargo
Commodities that are transported in large quantities and without packaging
- Dry bulk goods : non-liquid commodities (iron, coal and grain)
- Liquid bulk commodities : crude oil, petroleum products, chemicals
➔ General cargo
Goods that are consigned per item of package
- Break bulk : goods in small packaging (bags and boxes)
- Neo-bulk : various goods that are shipped and handled as a single item (steel products,
heavy machinery)
- Roll on / roll of : trucks and passenger cars that are driven onto and off ships via ramps
➔ Containers
- The standard container measure is 20 feet long, with a width and height of 8 feet
- Other lengths are 10 feet, 30 feet and 40 feet
- The 20-foot container is used as the standard unit size in which other variants are
expressed : the TEU or Twenty Feet Equivalent Unit
1.2.2.2 Classification by mode
Passenger transport
➔ Import criteria :
- Price
- Comfort
- Accessibility
- Speed
➔ The relationship between accessibility and speed is often inverse
- Private cares have an almost unlimited accessibility (both in time and space) compared to
trains and trams (because of the grid-like infrastructures)
- However, considering traffic congestion, what about the speed of transportation?
➔ Use of space by different modes in passenger transport :
Transportation mode Space required to Number of vehicles Average occupancy
transport 10,000 required to transport rate per vehicle
passengers per hour 1,000 passengers
Car 6-10 lanes 700 1.4 passenger
Bus 2-5 lanes 20 50%
Tram 1-2 tracks 13 75%
Underground 1 track / /
, Freight transport
➔ Model choice = f(type of goods, transportation distance)
Commodity type Distance
Continental intercontinental
Valuable goods 1 : road transport
st 1st: sea-transport
Perishable goods 2nd : rail transport 2nd : air transport
Fragile goods
Non-valuable goods (bulk Inland navigation and train 1ste : sea-transport
goods) 2nd : air transport
➔ New forms of transportation
- Short-sea shipping : maritime transportation over relatively short distances where no
oceans have to be crossed
- Intermodal systems : various forms of transportation are used (in order to achieve door-to-
door deliveries)
- Motorways of the sea
1.2.2.3 Scheduled and non-scheduled transport
➔ Scheduled transportation: public transport and scheduled airline flight
➔ Non-scheduled transportation: not operating according to a fixed schedule
1.2.2.4 Own-account transportation versus professional transportation
➔ Choice between transporting for own account and calling on a third party
➔ Passenger transport
- A choice between private and public transport
❖ Does the person have a car?
➔ Goods transportation
- A choice between own account and “third-party” transport services
1.2.3 Measuring traffic and transportation performance
1.2.3.1 Traffic performance versus transportation performance
Definitions
➔ Second method : quantity transported and distance of transporation
SECOND OF Traffic performance Transportation performance
METHOD
Passenger
Number of seat-kilometres (skm) Number of passenger kilometres (pkm)
transport
Commodity
Capacity tonne-kilometres (ctkm) Tonne-kilometres (tkm)
transport
1 The traffic and transport system
Derived demand
➔ Let us assume that a particular commodity is supplied at Antwerp (Sa) and is demanded in
Ghent (Dg). For a given quantity X the supplier is prepared to deliver the commodity at a price
OB. The buyer for his part, in accordance with the utility that he assigns to the product, is
willing to pay OC. The difference between the demand price and the supply price of the product
(OC – OB) provides the basis for calculating the costs of transportation. The difference
between the price at place of origin and the price at the destination determines the maximum
price the buyer is willing to pay to have the product transported form Antwerp to Ghent. If
transportation cost is greater than this difference, the he will no longer be willing to buy the
product. By confronting de demand and supply curves, we can derive the demand for
transportation (Dt). At a given quantity X, there is a willingness to pay a maximum price OT (=
OC – OB) for transportation. At a quantity Y, where the demand and supply curves for the
product intersect each other, there is no longer any price difference to serve as a basis for the
price of transportation. The demand curve for transportation (Dt) will intersect the X-axis in this
point.
,1.1 Preliminaries
➔ Traffic and transportation hardly ever arise spontaneously
➔ Traffic and transportation are the result of some other primary need for goods and services
➔ Traffic and transportation thus shows an intermediary character and it is a derived need
(derived nature)
➔ Graphical analysis : the derived nature of transport demand
- Starting situation: a commodity is supplied in Antwerp and demanded for in Ghent, and the
commodity thus needs to be transported
- Step 1: consider a quantity x (less than Y)
- Step 2: determine the delivery price OB
- Step 3: determine the willingness to pay OC
- Step 4: OC – OB gives the basics of calculating the MAXIMUM cost of transportation
- Step 5: derive Dt
- Step 6: assume St (upward sloping curve and based on marginal costs)
- Step 7: determine E (new quantity equilibrium taking into account transportation costs)
1.2 The traffic and transportation system
1.2.1 The difference between traffic and transportation
➔ Traffic consists of 2 components
- a) Means of transport: mobile capital goods like vehicles, trains, vessels, aeroplanes, etc.
- (b) Infrastructure: fixed capital goods
- (a) and (b) are PERMANENT COMPONENTS and result into a so-called traffic
performance
➔ Transportation takes into account the two permanent components of traffic plus the variable
component load
➔ Transportation thus exists of
- (a) Means of transport
- (b) Infrastructure
- (c) Load
1.2.2 Transportation subsystems
1.2.2.1 Classification by type of load
Passenger transport
Individual Common (gemeenschappelijk)
Private Car, bicycle, motorbike School buses, coach, services
Public Taxi Train, tram, bus, underground, plains
➔ Public transport : government-imposed regulations
, Freight transport
➔ Bulk cargo
Commodities that are transported in large quantities and without packaging
- Dry bulk goods : non-liquid commodities (iron, coal and grain)
- Liquid bulk commodities : crude oil, petroleum products, chemicals
➔ General cargo
Goods that are consigned per item of package
- Break bulk : goods in small packaging (bags and boxes)
- Neo-bulk : various goods that are shipped and handled as a single item (steel products,
heavy machinery)
- Roll on / roll of : trucks and passenger cars that are driven onto and off ships via ramps
➔ Containers
- The standard container measure is 20 feet long, with a width and height of 8 feet
- Other lengths are 10 feet, 30 feet and 40 feet
- The 20-foot container is used as the standard unit size in which other variants are
expressed : the TEU or Twenty Feet Equivalent Unit
1.2.2.2 Classification by mode
Passenger transport
➔ Import criteria :
- Price
- Comfort
- Accessibility
- Speed
➔ The relationship between accessibility and speed is often inverse
- Private cares have an almost unlimited accessibility (both in time and space) compared to
trains and trams (because of the grid-like infrastructures)
- However, considering traffic congestion, what about the speed of transportation?
➔ Use of space by different modes in passenger transport :
Transportation mode Space required to Number of vehicles Average occupancy
transport 10,000 required to transport rate per vehicle
passengers per hour 1,000 passengers
Car 6-10 lanes 700 1.4 passenger
Bus 2-5 lanes 20 50%
Tram 1-2 tracks 13 75%
Underground 1 track / /
, Freight transport
➔ Model choice = f(type of goods, transportation distance)
Commodity type Distance
Continental intercontinental
Valuable goods 1 : road transport
st 1st: sea-transport
Perishable goods 2nd : rail transport 2nd : air transport
Fragile goods
Non-valuable goods (bulk Inland navigation and train 1ste : sea-transport
goods) 2nd : air transport
➔ New forms of transportation
- Short-sea shipping : maritime transportation over relatively short distances where no
oceans have to be crossed
- Intermodal systems : various forms of transportation are used (in order to achieve door-to-
door deliveries)
- Motorways of the sea
1.2.2.3 Scheduled and non-scheduled transport
➔ Scheduled transportation: public transport and scheduled airline flight
➔ Non-scheduled transportation: not operating according to a fixed schedule
1.2.2.4 Own-account transportation versus professional transportation
➔ Choice between transporting for own account and calling on a third party
➔ Passenger transport
- A choice between private and public transport
❖ Does the person have a car?
➔ Goods transportation
- A choice between own account and “third-party” transport services
1.2.3 Measuring traffic and transportation performance
1.2.3.1 Traffic performance versus transportation performance
Definitions
➔ Second method : quantity transported and distance of transporation
SECOND OF Traffic performance Transportation performance
METHOD
Passenger
Number of seat-kilometres (skm) Number of passenger kilometres (pkm)
transport
Commodity
Capacity tonne-kilometres (ctkm) Tonne-kilometres (tkm)
transport