Linear Approximations and Differentials
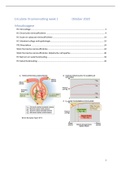
Suppose we want to approximate √2. Since we know the value of √1 we can use
the tangent line to 𝑦 = √𝑥 at the point (1,1) to approximate √2.
𝑦 = √𝑥
To do this we need to find the equation of the tangent line at (1,1) and then find
the 𝑦 value along the tangent line when 𝑥 = 2.
1
𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 𝑥 2
1 1
′( 1 −2
𝑓 𝑥) = 𝑥 =
2 2√𝑥
Slope of tangent line at 𝑥 = 1 is
1 1
𝑓 ′ (1) = =2.
2√1
, 2
Equation of tangent line at 𝑥 = 1:
1 1
𝑦 − 1 = (𝑥 − 1) or 𝑦 = (𝑥 − 1) + 1
2 2
1
1
𝐿(𝑥 ) = (𝑥 − 1) + 1 is the linear approximation of 𝑓(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 at 𝑥 = 1.
2
2
So we can approximate √2 by:
1 1
√2 ≈ 𝐿(2) = 2 (2 − 1) + 1 = 2 (1) + 1 = 1.5.
We can define the error in the linear approximation by:
actual value=approximate value +error, or equivalently:
error=actual value-approximate value.
The absolute error is then defined as:
Absolute error=|error|=|actual value-approximate value|.
The absolute error in our example is |𝑓 (2) − 𝐿(2)| = |√2 − 1.5|
≈ |1.4142 − 1.5| = 0.0858.
𝑒𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟 −0.0858
The percentage error is = ≈ −0.0607 = −0.6.07%.
𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 1.4142
If we wanted to approximate √0.5 , then put 𝑥 = 0.5 into 𝐿(𝑥)
1 1
√0.5 ≈ 𝐿(0.5) = 2 (0.5 − 1) + 1 = 2 (−0.5) + 1 = 0.75.