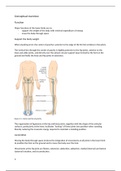
Key Terminology DiagramsHa
General Purpose – a computer system built for com
many different tasks.
Central Processing Unit m D
and
So
Computer System – made up of hardware and
The of the computer. sy
software, that work together for a common purpose.
Embedded system – a computer, built into a Carries out the FDE cycle; separ
machine, dedicated to one purpose. instruction fetched from the keybo
Execute
Fetch
memory, decoded, then Decode are
Input – entering data into a computer system.
performed.
Process – turning data into information.
Output – retrieving information from a computer Clock speed, cache and number of Input Process
system. cores all affect its performance,.
Hardware – the physical parts of a computer.
Enter data into aCPU turns data into
Software – the programs used to complete tasks on Memory computer system information by
a computer. through an input processing
Random Access
Memory (RAM)
Memory – used to hold data and instructions Volatile memory Non-volatile device. instructions.
Read Only Memory
temporarily – loses its data memory – stores
Secondary
Secondary
Storage – used
Storage
to storage
hold data and files
when the power its data, even
Secondary storage is long term where you is lost. when the power
long term.your data and files when the computer is
can keep Data can be is lost. Hardware
Input Devices
turned Solid
off. State written, changed Data can’t be
Optical Magnetic
(ROM)
or deleted. written or
Drives deleted. Keyboard Printe
Holds the current
Cost Optical is the cheapest option per GB. instructions, that Holds the Mouse Monit
are in use or instructions for
Speed Solid state are the fastest storage due to open. the boot-up Webcam Head
sequence to turn
no moving parts. Microphone Speak
Embedded Technology the computer on.
Scanner
Durability Solid state devices are the most durable. Computer systems, designed for one
Sensor Hybrid
purpose.
- No need for a
Portability Optical disks are the easiest and lightest
to move around. full operating Digital Cam
system. Photocopi
Capacity Magnetic generally hold the largest
amount of data.
- More reliable Touch scre
- Simpler to
Reliability Solid state devices usually last the design and
longest.
manufacture.
, Key Terminology Computer Systems (V2)
Computer system - Hardware and software, -the PC holds the
memory address
Diagrams
working together for a common purpose. Fetch Decode Execute cycle. CPU
turns the data into information CPU of the instruction.
Hardware – the physical parts of the Arith
through the FDE cycle. Control Unit
computer. 3 main components; ALU, CU and Cache.
Program
and
Data – raw figures entered into a computer CPU fetches instruction from memory, U
Counter
decoded by the control unit and then Accum
system. Registers
performsFactors;
the instruction.
cache, clock speed and cores.
Information – facts retrieved from a computer Memory Data Register M
The higher the clock speed, the more Address Register Current
system. cycles can be performed per second.
Embedded System – a system, built into a Instruction Register
The more cores, the more instructions
machine for a dedicated task. can be decoded at the same time.
CPU – the brain of the computer, which The bigger the cache size, the quicker Memory (RAM and RO
controls everything the computer does. the instructions can be accessed.
Primary Memory – holds instructions that are Memory -The memory holds the
in use. -Random instruction and data, The data
Volatile – temporary memory, which loses -Read Only travels through buses.
Access
- Non-volatile
data when the power is switched off.
Storage - Volatile
- Holds the boot
Non-volatile – long
Secondary storage term
stores memory,
data which
when it is not in does
use. - Holds
up sequence to o
Hardware
RAM
ROM
VIRTUAL GP Computer systems; s
Three
not types
lose of secondary storage are;
data. instructions
start the
magnetic,
Secondary solid-state
Optical
Storage andMagnetic
Solid- data
– stores optical
that is not
currently in
computer up. laptop, desktop PC, tablet.
State use.
devices.
currently in use but needed.
- If the RAM is full, o Embedded systems; auto
Cost Cheap Average Expensive
part of the HDD acts Nav, smartwatch, dishwash
Capacity Smaller Varies Large as virtual, temporary
machine.
capacity Real Life Technology
memory.
Reliabilit Reliable Highly Very reliable o Input devices; keyboard,
y in the reliable microphone, scanner, webc
short
term.
o Output devices; printer, m
Portabili Portable Portable Less portable speakers.
ty
Durabilit Damaged More Less durable o Internal components; he
y easily durable RAM, Graphics card, Hard D
Speed Slow Fast Slow power supply.