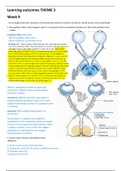
Chapter 8 Reproductive Function
Male Reproductive
1. Smooth muscle relaxation and shunting of blood into the sinusoids is
mediated by and results in a penile erection.
A) norepinephrine
B) nitroglycerine
C) nitric oxide
D) nicotinic acid
2. Priapism is a condition that causes ischemia as a result of:
A) circumcision trauma.
B) failure of detumescence.
C) tight retracted foreskin.
D) fibrous plaque in the penis.
, 3. Common risk factors for erectile dysfunction due to generalized penile
arterial insufficiency include:
A) cryptorchidism.
B) cigarette smoking.
C) testicular torsion.
D) benign prostate hypertrophy.
4. Squamous cell cancer of the penis is more likely to develop in men with
chronic:
A) erectile dysfunction.
B) herpes ulcerations.
C) Peyronie disease.
D) smegma accumulation.
5. In a hydrocele, excess fluid is present in the:
A) epididymis.
B) tunica vaginalis.
C) pampiniform plexus.
D) vas deferens ampulla.
6. Testicular torsion, a serious disorder affecting young male individuals,
causes:
A) inguinal herniation.
B) cancer of the scrotum.
C) dartos muscle atrophy.
D) loss of testicular perfusion.
7. Men older than age 50 are at high risk for prostatic hypertrophy with
complications that include:
Male Reproductive
1. Smooth muscle relaxation and shunting of blood into the sinusoids is
mediated by and results in a penile erection.
A) norepinephrine
B) nitroglycerine
C) nitric oxide
D) nicotinic acid
2. Priapism is a condition that causes ischemia as a result of:
A) circumcision trauma.
B) failure of detumescence.
C) tight retracted foreskin.
D) fibrous plaque in the penis.
, 3. Common risk factors for erectile dysfunction due to generalized penile
arterial insufficiency include:
A) cryptorchidism.
B) cigarette smoking.
C) testicular torsion.
D) benign prostate hypertrophy.
4. Squamous cell cancer of the penis is more likely to develop in men with
chronic:
A) erectile dysfunction.
B) herpes ulcerations.
C) Peyronie disease.
D) smegma accumulation.
5. In a hydrocele, excess fluid is present in the:
A) epididymis.
B) tunica vaginalis.
C) pampiniform plexus.
D) vas deferens ampulla.
6. Testicular torsion, a serious disorder affecting young male individuals,
causes:
A) inguinal herniation.
B) cancer of the scrotum.
C) dartos muscle atrophy.
D) loss of testicular perfusion.
7. Men older than age 50 are at high risk for prostatic hypertrophy with
complications that include: