Introduction
Homeostasis
● The ability to maintain stability within limits
● Balance, equilibrium
○ Not quite at point of equilibrium
● Small internal fluctuations inside human bodies
○ Control systems
■ Control your physiology
● All of your other organ systems are controlled by these
■ Involuntary control
■ Autonomic nervous system
■ Endocrine system
● Large external fluctuations outside body
○ Even though you have these large
external fluctuations outside of
your body, there is a narrow limit
of change
○ Control systems enable these
small internal fluctuations
● Homeostasis is the maintenance of a
relatively constant internal state regardless of changes in the external
environment
○ Relatively constant means not exactly equilibrium
○ Up regulation
■ When an organ system works faster or harder
○ Down regulation
■ Decreasing the intensity that the organ system works
○ To get back to homeostasis, need to either down regulate or up regulate
■ In the body, if you get either up or down regulation and the body
does the opposite, you never truly get back to where you were
■ If you get down regulation, the control systems will work to up
regulate it, it will up regulate and it will be slightly off, it won’t be
exactly the same
● Claude Bernard’s Concept
○ Homeostasis was first defined by Claude Bernard
, ■ He came up with 4 concepts
○ All organs interact
■ All organs are connected
■ The heart is connected with every other organ system
■ One system goes down, everything else goes down
○ All cells of organs bathed in internal fluid
■ Organs are made up of cells
■ Cells have internal fluid called cytoplasm
● Very important that the cytoplasm is consist in quality and
quantity
● The quality and quantity of fluid must remain relatively
constant inside the cell
○ Cells exist if fluid remains constant in quantity and quality (osmosis)
○ Fluctuations occur within narrow limits
■ If there is a large change, there is no homeostasis
■ 290 ∓ 5 mOsm is the narrow range
● Osmosis is the diffusion of water from where water is in high concentration to
where water is in low concentration
○ Talking about the movement of water, no ions
○ Example: There are two baths, Bath 1 and Bath 2
■ Each of them have exactly the same volume of water
■ Salt, which is made up of ions, is added to Bath 1
■ Bath 1 has a higher concentration of ions
■ Bath 2 has a lower concentration of ions
■ Bath 2 has a higher concentration of water
● This is because it doesn’t have any salt dissolved in it
■ The water flows from Bath 2 to Bath 1
○ Water follows salt (solute)
○ Concentrate is the number of ions in solution
■ Can major in units
○ The units for concentration are called osmotes
■ Not used referred to as this in biology and cells
○ In biology and cell, the the units for concentration are called miliosmotes
(mOsm)
■ This is because of very small differences in concentration
○ Example: Bath 1 has 290 mOsm in it and Bath 2 has 230 mOsm
■ Bath 2 is more dilute, it has a higher concentration of water
■ Water follows the higher concentration of ion
○ How does this relate to the human body? Here’s how in an example:
, ■ There is a blood vessel and a normal body cell
■ Body cells have cytoplasm
● The fluid has ions and proteins dissolved in it
● Cells are also concentrated
● Ions and proteins
● Normal concentration of a human body cell is 290 mOsm
● The body tries to maintain homeostasis so 290 mOsm will
change but not by much
● Range of change is 290 ∓ 5 mOsm (range is 285-295)
■ Blood is concentrated
● Has ions and proteins
● Blood is an equilibrium with cell in terms of centration
● 290 mOsm is the normal concentration
■ The space between the cell and the blood vessels is the
interstitium
● Interstitium has concentration of 290 mOsm
● Has proteins and ions
● Everything is an equilibrium, the cell, the blood, and the
equilibrium
○ Example:
■ When you run, you start to perspire
■ When your perspire, if you don’t replenish that water, you start to
feel drowsy, lethargic
■ The water is coming out of your cells, but the water is actually
coming out of your blood
■ When you perspire and dehydrate, you actually lose blood volume
● This is because a lot of the fluid in blood is water
● When the volume of the blood goes down, the number of
ions stays the same
● Because there is less fluid, but the same number of proteins
and ions in the blood, the number of the concentrate, 290
mOsm, goes up
● The fluid becomes more concentrated
● In this example, it went up to 293
■ The water is going to go into the blood from the interstitium
● It’s going to keeping going into the blood until there is
equilibrium between the interstitium and the blood
■ As water goes into the blood, the number of concentration is going
to go down
, ■ As the water leaves the interstitium, the number of concentration is
going to go up
■ Now the blood and interstitium are at an equilibrium of 291.5 mOsm
■ Now there is no more movement of water in and out of that blood
vessel
■ If the interstitium is at 291.5 and the cell is at 290, the water is
going to go out of the cell
■ The concentration of the water is going to go up to 290.75
■ The concentration of the interstitium is going to go down to 290.75
■ The end result of making the blood more concentrated was making
the cell more concentrated too (the big picture)
○ Water goes towards the higher number of concentration
○ Whatever happens in the blood happens in the cell
■ If the blood becomes more concentrated, the cell becomes more
concentrated
■ If the blood becomes more dilute, the cell becomes more dilute
○ Blood brings oxygen and nutrients to cells
○ Because blood goes everywhere in your body, if you become dehydrated,
if you don’t replenish your thirst, you could potentially start killing off your
body cells, which would be the end result
○ Quality affects quantity
■ Quality means concentration
■ What is the quality of the fluid
● Is it concentrated or dilute?
■ The more the concentration difference, the greater the difference in
quality across a biological membrane, the more quantity, the more
fluid, moves across that biological membrane
■ If there is no difference is quality across that biological membrane,
there is no difference in fluid movement, there is no difference in
quantity across that biological membrane
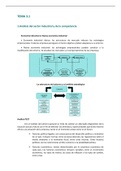
Feedback Mechanisms
● Physiology works by feedback mechanisms
● All feedback mechanisms have a disturbance, a control system, a sensor, and
either an amplifier or inverted amplifier
● All the body does is react to stimuli
○ It is reactive, it is not proactive
○ All the body does is detect stimuli and react to them
○ The body only reacts if it absolutely has to