Chapter 2 Neuroscience totalkaboutinclass
Neuroscience howbrain nervoussystemaffectmentalprocesses andbehavior iii
how doesbraincommunicate vocabulary
info
important
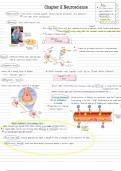
Neurons cellsthattransmitinfo
Also gliacellsbraincellsgiveimportantfunctiontoñÉuÉns donotconductnerveimpulses
formmyelin fattywaxystuffthatsurroundsneuronssosingnalmovefaster
Nomyelinmultiplesclerosis
Neariratomy
canbehundredmicrometersmanycentimeters
axons
re chemical
messengerscarryneural acrosssynapse
signals
apse connectionformedwhenaxon
bulbgets
closeto dentriteoranotherneuron
Inenection
hasna
are
synapticneuron
euronthatissendingsignalatsynapse eachneuroncansynaps with upto 10,000otherneurons
synapticgap the
signs
sostsynaptic neuron
euronthatreceivessignalat a synapse Brainuseselectrochemicalenergymadebyions sig
off
nagging
Braintissue gliacellsneuronssurroundedbyfluidwithdifferentions
restingpotential whenneuronisrestingionchannelsstopNat sodium
thedifference fromgoinginthecell highconcentrationofNatmakeouts
in charge conornegative
cellhigh
cellpositiveInside ionsnegativecharge
important in creating
neuralsignals
Aerotentialshownearonsfired
whenneuronsgetsignalsfromotherneuronsitcanmakecellmore tort
if signalmakesneuronmore t mayreachthresholdofexcitation ssmv
ionchannelsopenallowNattoenter
allornonelaw allactionpotentialsareequalinstrengthsowhenisfiredgoesallthewaydowntheaxon
refractoryperiod brieftimeafter
neuronfired doitagain
actionpotentialitcant
, synaptic
transmission
actionpotentialreachesaxonbulb neurotransmittersintosynaps
comein contactwithreceptors changein electricalpotential
lock3Key
excitation whenneurotransmittermakespostsynapticcellmorepositiveinsidemorelikelyto
fireactionpotential Glutamate
VS
inhibition causesinsideorpostsynapticcelltobecomemorenegativetomoveawayfromthresholdofexcitation
GABA
axon addsupthe two signalsandonlywhenthesummovesrestingpotential
to threshold theneuron will fire actionpotential
reuptake neurotransmitters removedfrom synapse3returned topresynaptic
chemicalmessengers
in theBrain 2.2
neuro
modulator chemicalsthataffectsignalingwithout
directlychangingrestingpotential
the1stneurotransmitterdiscovered Acetylcholine Acn
consciousnessand
inhibitsactionofheart exciteskeletalmuscles memory
pplw alzheimer'slackneuronsreleasingAch
Dopamine Serotonin
neurotransmitter movementmotivation neurotransmitter sleeparousalmood
learningandreward eatingpainperception
Parkinson's lossordopamine lackofserotonin depression anxiety
schizophreniatoomuchdopamine drugspreventitsreuptake
releaseshormone
norepinephrine nor adrenaline
neurotransmitter regulatesleeparousalmood energyattention
ammaaminobutyricacidGABA marinnibitoryneurotransmitter inbrainRegulatearousal
lutamate manexciatoryneurotransmitter inbrainFoundin 50 ofsynapsestoomuchcankillbraincells
Endorphins
neuromodulatorsthatactlikenaturalpainkillers
similartoopiatesopiumheroinmorphinecodein
releasedincuswhenstressedphysicalexertionorinjury
structure or
nervoussystem
cons brain's
Centralnervoussystem spine
peripheral nervoussystem Pns allnervoussystembsbutbrainandspine