CATALYSTS ↳
↳
save
save
money
energy
↳
eg zeolite :
largeS A
A substance that by
increases the rate of reaction
providing
an alterative that has lower activation
pathway a energy
.
It is
chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction
.
bond with the active sites on me
surface of the catalyst
/
W
substances adsorb to the surface desorption -
molec
Catalyst in a different statel >
- -
=
HETEROGENEOUS-phase from the reactants of solid heterogeneous catalysts reaction
from the surface
lowers activation occurs
Soli
aest energy
have
so more particles
enough energy
e
.
g N2(g) + 34 =(g) >
-
2NHz (g) potential
*
.
M
energy
4 SA of Catalyst =
↑rate of reaction
reactants
H OMOGENEOUS-reactants
catalyst in the same phase as the
- products
S
progress
aqueous
-
>
generally in aqueous reactants
-
combine
reformed
form intermediate species :
reactants catalyst ->
products +
catalyst
2nd bump-
Y energy required
to
break up intermediast
internedes
a
USES OF CATALUSTS
INDUSTRY : ENVIROMENTALLY :
↑ pressure ↑rate molecules per unit
CO2/ CO2/
↳ lower ↳
temp-less money lower temp/pressure required -
less energy
better atom
↳ ↳ less
speeds reaction waste produced-economies CATALYTIC CONVERTERS -
reduce levels of pollut
made of rhodium , platinum and palladium alloy
↳
changes properties of products 200 + 2 >
2CO2 + N
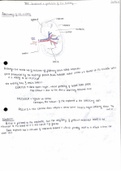
MAXWELL-BOLTIM
Conc . or volume of ractant/product made
RATE OF REACTION unit time
HOW MSUR
I snowing energy in
gas particles
measure mass lost
HOW LONG IT TAKES
use a fine cupboard
any namful/toxic 10 of 1
likely
for ·
gas Molecules most
- energy of a
particle
O
M
in a sample
ELECTICAL
conductiveenvit
↳
VOLUME OF GAS ·
mean energy of
PRODUCED Syringe ↳
particles
IN-H t
to get +he if Ations are o
used up
>
Po
- conc
produced
TITRATION -
CHANGE being
a H+ H
+
↓
area total 10
PH pH will change -
under = of Molecules
↓ sech ladd uchencas
curve in sample
ac
absorbance/conc
-
COLORIMETRY - graph
12 + CH3(OCH >
- (MyCoc42 +
1- + H
+
=
-
brown colourless colourless L
W
O starts at 0, 0