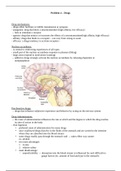
- Purpose of eating
= supplying the body with molecular building blocks & energy for function/survival
- Digestion
= gastrointestinal process of breaking down food & absorbing it constituents into the body
Basic steps of digestion
1. Chewing
increasing surface area, break up food
2. Addition of saliva in the mouth
amylase begins digestion & lubrication
3. Peristaltic movements
movement in digestion system that moves food
4. Stomach
hydrochloric acid continues digestion, storage of food, pepsin for amino acids
5. Duodenum
upper part of intestine, absorption of simple sugars, breakdown of protein into
amino acids, emulsification of fats (bile),
6. Intestine
resorption of water and electrolytes
Much of the digestion is supported by microbiome (bacteria/organisms)
Energy is consumed at specific times, but the energy use of the body is continuous
urge for storage of energy
Lipids = fat 85%
Can store the most energy, without water (compact) most efficient
Amino acids = proteins 14%
Glucose = glycogen rare
3 phases of energy metabolism
- Cephalic phase
Preparatory phase, initiated by the sight, smell, taste, thought of food
- Absorptive phase
Consumed food’s energy is absorbed into the bloodstream meets the bodies immediate
needs.
- Fasting phase
All absorbed energy from last meal has been used energy for life processes has to be
withdrawn from reserves to meat energy requirements.
Skip fasting phase rapid weight gain
, The flow of energy during energy metabolism is controlled by pancreatic hormones
o Insulin
During cephalic/absorptive phase
- Glucose as energy source in cells
- Promotes storage of glucose
glycogen in liver/muscles, fat in adipose tissue, protein in muscle
- Lowers levels of bloodborne fuels
o Glucagon
during fasting phase
- Conversion of glycogen & protein into glucose (gluconeogenesis)
- Glucose is mainly saved for brain
- The body can use ketones (converted from free fatty acids)
Theories of hunger
o Set point assumption
- Hunger is caused by an energy deficit
- Eating returns energy to an optimal level (=set point)
- Based on negative feedback principles (compensatory effects in opposite direction)
Analogy = thermostat regulated heating
set point mechanism; defines optimal level
Detector mechanism; detects deviation
Effector mechanism; eliminates deviation
Glucostatic set point theory
The idea that we get hungry when blood glucose levels drop (primary source of energy for
brain)
meal initiation
Lipostatic set point theory
The idea that when fat levels rise or fall compared to the set point, compensatory
adjustments in eating behavior come into play. (Based on relatively stable bodyweight)
long term regulation
Criticism
- Brain is plastic, can alter energy need, set point theory is less relevant
- Epidemic obesity wouldn’t exist if everything would return to a set point
- Does not explain diabetic hunger whilst having high glucose levels
- Experiments drop glucose levels to unrealistically low concentrations in order to
evoke eating behavior
- The theory fails to recognize sight/smell/taste/learning
- In evolution people had to create reserves for scarcity eat past set-point