1. Acids and bases: Bronsted-Lowry concept, Lewis concept, strengths of acids, strong &
weak acids and bases, pH, buffer solutions. Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, buffering
against pH changes in biological systems, maintaining the pH of blood.
Bronsted-Lowry concept
The Brønsted–Lowry definition, formulated in 1923, independently by Johannes Nicolaus
Brønsted in Denmark and Martin Lowry in England,
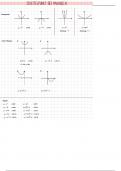
In an acid–base reaction, the removal of a hydrogen ion from the acid and its addition to the base.
The removal of a hydrogen ion from an acid produces its conjugate base, which is the acid with a
hydrogen ion removed. The reception of a proton by a base produces its conjugate acid, which is the
base with a hydrogen ion added.
The general formula for acid–base reactions according to the Brønsted–Lowry definition is:
HA + B → BH+ + A−
where AH represents the acid, B represents the base, BH + represents the conjugate acid of B, and
A− represents the conjugate base of HA.
For example, a Brønsted-Lowry model for the dissociation of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in aqueous
solution would be the following:
HCl + H2O H3O+ + Cl−
The removal of H from the HCl produces the chloride ion, Cl−, the conjugate base of the acid. The
+
addition of H+ to the H2O (acting as a base) forms the hydronium ion, H3O+, the conjugate acid of the
base.
Lewis definition
Lewis defines a base (referred to as a Lewis base) to be a compound that can donate an electron
pair, and an acid (a Lewis acid) to be a compound that can receive this electron pair.
For example, a silver cation behaves as an acid with respect to ammonia, which behaves as a base,
in the following reaction:
Ag+ + 2 :NH3 → [H3N:Ag:NH3]+
The result of this reaction is the formation of an ammonia–silver adduct.
Strength of Acids and Bases
The strength of an acid refers to its ability or tendency to lose a proton (H+).
Strength of acids are two types: Strong acids and weak acids.
about:blank 1/7
, 6/11/24, 8:33 PM 4. Acids and Bases W - Lecture notes 1,2,3
Strong acids: A strong acid is one that completely ionizes (dissociates) in a solution.
In other words, one mole of a strong acid HA dissolves in water yielding one mole of
H+ and one mole of the conjugate base, A−.
Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl), hydroiodic acid (HI), hydrobromic
acid (HBr), perchloric acid (HClO4), nitric acid (HNO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). In water
each of these essentially ionizes 100%.
Weak acids: A weak acid only partially dissociates in a solution.
examples include carbonic acid (H2CO3) and acetic acid (CH3COOH). At equilibrium
both the acid and the conjugate base are present in solution.
Stronger acids have a larger Ka and a smaller pKa than weaker acids.
The stronger an acid is, the more easily it loses a proton, H +. Two key factors that
contribute to the ease of deprotonation are the polarity of the H—A bond and the size of
atom A, which determines the strength of the H—A bond.
Write down the Short note on pH
Answer: The concept of p[H] was first introduced by Danish chemist Søren Peder
Lauritz Sørensen at the Carlsberg Laboratory in 1909 and revised to the modern pH in
1924 to accommodate definitions and measurements in terms of electrochemical cells.
The exact meaning of the "p" in "pH", according to the Carlsberg Foundation pH stands
for "power of hydrogen". It has also been suggested that the "p" stands for the potential
hydrogen. Current usage in chemistry is that p stands for "decimal cologarithm of", as
also in the term pKa, used for acid dissociation constants.
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution.
Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater
than 7 are basic or alkaline. Pure water has a pH very close to 7.
Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with
transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and
a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode. Measurement of pH for
aqueous solutions can be done with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or using
indicators.
pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry,
food sciences,environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical
engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications.
Mathematically,
about:blank 2/7