NUR 325 Exam 3 Questions and Answers 100% Verified
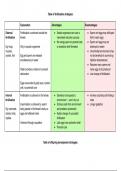
A 45-year-old male client with leg ulcers and arterial insufficiency is admitted to the hospital. The nurse understands that leg ulcers of this nature are usually caused by: a. Decreased arterial blood flow secondary to vasoconstriction b. Decreased arterial blood flow leading to hyperemia c. Atherosclerotic obstruction of the arteries d. Trauma to the lower extremities - ️️A (Decreased arterial flow is a result of vasospasm. The etiology is unknown. It is more problematic in colder climates or when the person is under stress. Hyperemia occurs when the vasospasm is relieved.) A 45-yr-old man with asthma is brought to the emergency department by automobile. He is short of breath and appears frightened. During the initial nursing assessment, which clinical manifestation might be present as an early manifestation during an exacerbation of asthma? a. Anxiety b. Cyanosis c. Bradycardia d. Hypercapnia - ️️A (decreased CO2 because hyperventilating) A 57-year-old client with a history of asthma is prescribed propranolol (Inderal) to control hypertension. Before administered propranolol, which of the following actions should the nurse take first? a. Monitor the apical pulse rate b. Instruct the client to take medication with food c. Question the physician about the order d. Caution the client to rise slowly when standing - ️️C (Propranolol and other betaadrenergic blockers are contraindicated in a client with asthma, so the nurse should question the physician before giving the dose. The other responses are appropriate actions for a client receiving propranolol, but questioning the physician takes priority. The client's apical pulse should always be checked before giving propranolol; if the pulse rate is extremely low, the nurse should withhold the drug and notify the physician.) A 60-year-old male client comes into the emergency department with complaints of crushing chest pain that radiates to his shoulder and left arm. The admitting diagnosis is acute myocardial infarction. Immediate admission orders include oxygen by NC at 4L/minute, blood work, chest x-ray, an ECG, and 2 mg of morphine given intravenously. The nurse should first: a. Administer the morphine b. Obtain a 12-lead ECG c. Obtain the lab workd. Order the chest x-ray - ️️A (Although obtaining the ECG, chest x-ray, and blood work are all important, the nurse's priority action would be to relieve the crushing chest pain.) A 72-year-old man presents to the emergency room. The patient appears diaphoretic and anxious, and has noted peripheral edema. The patient's vital signs are blood pressure of 100/40, heart rate of 130 and irregular, and respiratory rate of 26. How does the nurse interpret these findings? a. The patient is having a myocardial infarction. b. The patient has impaired central perfusion. c. The patient has a virus. d. Pain medication should be administered to this patient. - ️️B (This patient has the classic symptoms of impaired central perfusion. Central perfusion occurs when cardiac output is optimal and blood is pumped to all of the organs and tissues from the arteries, through the capillaries, and then back to the heart through the veins. The nurse needs to administer oxygen. Chest pain is often present with myocardial infarction, along with elevated blood pressure readings and electrocardiogram changes. Viral illness commonly presents with other symptoms such as body ache or gastrointestinal issues, and typically has little or no effect on the heart rate. Pain management is not indicated for patients who do not present with pain. Also, the question is asking what assessment the nurse has made, and is not asking about interventions.) A client comes to the outpatient clinic and tells the nurse that he has had legs pains that began when he walks but cease when he stops walking. Which of the following conditions would the nurse assess for? a. An acute obstruction in the vessels of the legs b. Peripheral vascular problems in both legs c. Diabetes d. Calcium deficiency - ️️B (Intermittent claudication is a condition that indicates vascular deficiencies in the peripheral vascular system. If an obstruction were present, the leg pain would persist when the client stops walking. Low calcium levels may cause leg cramps but would not necessarily be related to walking.) A client enters the ER complaining of chest pressure and severe epigastric distress. His VS are 158/90, 94, 24, and 99*F. The doctor orders cardiac enzymes. If the client were diagnosed with an MI, the nurse would expect which cardiac enzyme to rise within the next 3 to 8 hours? a. Creatine kinase (CK or CPK) b. Lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) c. LDH-1 d. LDH-2 - ️️A (Creatine kinase (CK, formally known as CPK) rises in 3-8 hours if an MI is present. When the myocardium is damaged, CPK leaks out of the cellmembranes and into the bloodstream. Lactic dehydrogenase rises in 24-48 hours, and LDH-1 and LDH-2 rises in 8-24 hours.) A client enters the ER complaining of severe chest pain. A myocardial infarction is suspected. A 12 lead ECG appears normal, but the doctor admits the client for further testing until cardiac enzyme studies are returned. All of the following will be included in the nursing care plan. Which activity has the highest priority? a. Monitoring vital signs b. Completing a physical assessment c. Maintaining cardiac monitoring d. Maintaining at least one IV access site - ️️C (Even though initial tests seem to be within normal range, it takes at least 3 hours for the cardiac enzyme studies to register. In the meantime, the client needs to be watched for bradycardia, heart block, ventricular irritability, and other arrhythmias. Other activities can be accomplished around the MI monitoring.) A client has driven himself to the ER. He is 50 years old, has a history of hypertension, and informs the nurse that his father died of a heart attack at 60 years of age. The client is presently complaining of indigestion. The nurse connects him to an ECG monitor and begins administering oxygen at 2 L/minute per NC. The nurse's next action would be to: a. Call for the doctor b. Start an intravenous line c. Obtain a portable chest radiograph d. Draw blood for laboratory studies - ️️B (Advanced cardiac life support recommends that at least one or two intravenous lines be inserted in one or both of the antecubital spaces. Calling the physician, obtaining a portable chest radiograph, and drawing blood are important but secondary to starting the intravenous line.) A client is receiving spironolactone to treat hypertension. Which of the following instructions should the nurse provide? a. "Eat foods high in potassium." b. "Take daily potassium supplements." c. "Discontinue sodium restrictions." d. "Avoid salt substitutes." - ️️D (Because spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic, the client should avoid salt substitutes because of their high potassium content. The client should also avoid potassium-rich foods and potassium supplements. To reduce fluid-volume overload, sodium restrictions should continue.) A client is wearing a continuous cardiac monitor, which begins to sound its alarm. A nurse sees no electrocardiogram complexes on the screen. The first action of the nurse is to: a. Check the client status and lead placementb. Press the recorder button on the electrocardiogram console c. Call the physician d. Call a code blue - ️️A (Sudden loss of electrocardiogram complexes indicates ventricular asystole or possible electrode displacement. Accurate assessment of the client and equipment is necessary to determine the cause and identify the appropriate intervention.) A client who has been receiving heparin therapy also is started on warfarin. The client asks a nurse why both medications are being administered. In formulating a response, the nurse incorporates the understanding that warfarin: A. Stimulates the breakdown of specific clotting factors by the liver, and it takes 2-3 days for this to exert an anticoagulant effect. B. Inhibits synthesis of specific clotting factors in the liver, and it takes 3-4 days for this medication to exert an anticoagulant effect. C. Stimulates production of the body's own thrombolytic substances, but it takes 2-4 days for this to begin. D. Has the same mechanism of action as Heparin, and the crossover time is needed for the serum level of warfarin to be therapeutic. - ️️B (Warfarin works in the liver and inhibits synthesis of four vitamin K-dependent clotting factors (X, IX, VII, and II), but it takes 3 to 4 days before the therapeutic effect of warfarin is exhibited) A client with no history of cardiovascular disease comes into the ambulatory clinic with flu-like symptoms. The client suddenly complains of chest pain. Which of the following questions would best help a nurse to discriminate pain caused by a non-cardiac problem? a. "Have you ever had this pain before?" b. "Can you describe the pain to me?" c. "Does the pain get worse when you breathe in?" d. "Can you rate the pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst?" - ️️C (Chest pain is assessed by using the standard pain assessment parameters. Options 1, 2, and 4 may or may not help discriminate the origin of pain. Pain of pleuropulmonary origin
Escuela, estudio y materia
- Institución
- NUR 325
- Grado
- NUR 325
Información del documento
- Subido en
- 10 de junio de 2024
- Número de páginas
- 103
- Escrito en
- 2023/2024
- Tipo
- Examen
- Contiene
- Preguntas y respuestas
Temas
-
nur 325
Documento también disponible en un lote