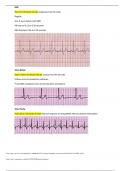
a company’s main…
s-strengths
w-weakness
o-opportunities
t-threats
A product is only a tool to solve a costumer problem.
Exchange = the act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering
something in return. Example: a political candidate wants votes.
Core marketing activities:
- Consumer research
- Product development
- Communication
- Distribution
- Pricing
- Service
Marketing management = the art and science of choosing target markets and
building profitable relationships with them.
2 important questions for marketing manager:
1. What costumers will we serve?
2. How can we serve these costumers the best?
Marketing management is customer & demand management.
Marketing myopa = the mistake of paying more attention to the specific products
you’re selling than to the benefits and experiences which comes because of this
product.
They forget that a product is just a tool to solve a costumers’ problem.
5 marketing management orientations:
1. The production concept (oil, raw materials, services). Consumers will favour
products that are highly available and affordable organisations should
focus on improving efficiency of production and distribution.
2. The product concept (oil, raw materials, services). Consumer will favour
products with the most quality organisation should focus on continue
product improvement.
3. The selling concept (energy, insurance, mobile phone subscription). Goal is to
sell what the company makes, rather than marketing what the consumer
wants. (blood donations, funeral insurance).
4. The marketing concept (Toyota, Unilever, Ikea, L’Oréal). A philosophy in
which achieving organisational goals depends on knowing the needs and
wants of target customer (consumer) and delivering the desired satisfactions
(pleasure) better than competitors do. Focus on customer needs + wants.
‘We don’t have a marketing department, we have a customer department.’
, Instead of ‘make & sell philosophy’ a ‘sense & respond philosophy’.
5. The societal marketing concept (Body Shop, Tony Chocolonely). Company’s
marketing should consider:
a. Consumers’ wants
b. Company’s requirements
c. Consumer long-run interest
d. Society long-run interest
- Sustainable marketing = responsible marketing (socially & environmentally)
that meets the needs of now and the future.
- Shared value = creating economic value that also creates value for society.
companies need 3 considerations for their marketing strategy:
1 company profits
2 consumer wants
3 society’s interest/human welfare
Preparing a marketing programme
When a company knows which costumers to serve and how to create value for them,
it is time to develop a marketing program. You use the marketing mix, the set of tools
classified in 4 groups: the 4 P’s:
product: company needs to create a need-satisfying market offer
price: how much will you charge for the offering?
place: how will you make the offering available for target group?
promotion: engage target products, communicate about offering, persuade
costumers.
Building customer relationships
When you used all the marketing strategies and they worked it is time to get the
most important part done: building and managing customer relationships.
-customer relationship management = building and maintaining profitable customer
relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction
Customer value: customer compares all offers from comparable offers and
choose on perceived value. They compare all benefits and costs of an offer.
This is very personal. I want a cheap secondhand car while Joost wants a
Tesla (electric + fashion, mine ugly + polluting). Same product (car) but
different values of owning the car.
Customer satisfaction: when you buy a HP laptop you hope you will be happy
with it and it works the way you thought. When it is alright: you happy so
satisfied. When it is disappointing, you are dissatisfied.
Clearly: the more satisfied customers are, the more profit the company will feel in
economic performances because of their marketing.
Smart companies deliver more than they promised customers will be extra
surprised and satisfied! (Oh I didn’t know it has this function!)
Happy customers will come back as well as become ‘willing marketing partners’ by
spreading the word.
Customer relationship levels & tools
Companies can build customers relationships at many levels.
-phone/calling (not many companies do this)
-website/social media (followers!)
, -markets with few customers are high margins full partnerships with key
customers (Ben&Jerry’s with Albert Heijn & Publix).
-frequency marketing programmes (appreciate customers who buy often).
Example: KLM frequent flyer (flying blue), BMW club.
Engaging customers
*Customer-engaged marketing = making the brand a meaningful part of consumers’
conversations and lives.
Customers connect with companies by internet and social media marketing.
Companies are on every social media channel to create brand buzz. They post
things, hope they go viral, will reach as many customers as possible.
Ikea: 1st one who tags this wins a bed, they get 10000 online reactions). People
share it, talk about it, it is in their lives.
Companies cannot longer rely on marketing by intrusion but need to practice
marketing by attraction (create offerings and messages that engage consumers,
rather than interrupt them).
*Consumer-generated marketing = brand exchanges created by consumers
themselves (invited and uninvited) where consumers are playing an increasing role
in shaping their own brand experiences and those of other consumers. This might
happen by customer-to-customer exchange in…
-blogs, video sharing, social media
-companies are asking consumers for new product ideas or inviting customers to
play a role in shaping ads.
For companies this takes a lot of time and costs, and inviting consumers (opinions)
can backfire (in a negative way for the brand).
Summary: through social media consumers are playing a growing role in shaping
their brand experiences and engaged consumers are having a say in product design,
usage and packaging to brand messaging, pricing and distribution. Brands must
embrace this, otherwise they risk being left behind.
Partner relationship management = working closely with others inside & outside the
company to jointly engage and bring more value to customers.
No matter what your job in the company is, you must understand marketing and be
focused on customers.
Marketers must work together with suppliers, channel partners and others outside
the company.
Summary chapter 3
Analysing the marketing environment
Marketing environment = the actors and forces outside marketing that affect
marketing management’s ability to build and maintain successful relationships with
target customers.
A trade war is when a country imposes tariffs or other barriers on imported products,
prompting other countries to retaliate by implementing similar taxes or penalties.
You raise the price of the goods that are coming in.