-Lowest hierarchy is at the organelles within a cell
-Cells with the same functions collected into larger groups -> tissues
-Tissues are collected into organs which carry out a single task
-Organs work together in organ systems that perform large-scale functions
Cell Parts
-Organelles -> cell parts that function within a cell
oCoordinate with other organelles to perform a cell’s basic functions
-Ribosomes -> carry out protein synthesis
-Golgi Apparatus -> modifies & packages proteins secreted from a cell
-Mitochondria -> convert energy present in chemical bonds of food accessible to the cell
-Nucleus -> stores & processes instructions contained in the DNA that tell the cell what its
functions are
Cells
-Smallest living unit of life
-In humans, some cells function autonomously; ex. Phagocytic white blood cells
-Cells highly specialized to perform a specific function
Organs
-Structures composed of several types of tissues & perform one or more functions
Organ Systems
-Functional units composed of several organs
-Functions include: digestion of food, circulation of nutrients, removal of wastes, &
reproduction Vocab:
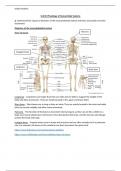
-Anatomical Position: standard positioning of the body as standing; feet together; arms to
the side; with head, eyes, and palms of hands forward
-Cells: the basic structural unit of an organism from which living things are created
-Cellular functions: Processes that include growth, metabolism, replication, protein
synthesis, and movement
-Directional Terminology: Words used to explain relationships of locations of anatomical
elements
-Organelle: a specialized part of a cell that has a specific function
-Organ: a self-contained part of an organism that performs a specific function
-Reference planes: Planes dividing the body to describe locations: sagittal, transverse, and
coronal
-Tissue: a group of cells with similar structure that function together as a unit, but at a
lower level than organs
-Superior: Toward the head/upper part of a structure (bird’s-eye view, looking down)
-Inferior: Away from the head/lower part of a structure (bottom view, looking up)
-Lateral- Farther from midline -Medial- Nearer to midline
-Superficial- Close to the surface of the body.
-Deep- Away from the surface of the body
-Proximal- Nearer to the origination of a structure.
-Distal- Farther from the origination of a structure.
-Anterior- At or near the front of the body
-Posterior- At or near the back of the body
-Prone- Patient laying on their belly, arms that the side.
-Supine- Patient laying on their back, arms that the side.
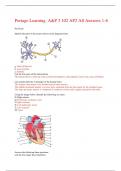
Circulatory System – Khan Academy
Jobs of the heart:
-Systemic flow (entire body)
-Pulmonary Flow (blood to & from the
lungs)
Coronary blood vessels
-Serving the heart muscle itself
-Serve the needs of cells
-Fall under the category of systemic
flow
Vein = blood going towards the heart Artery = blood going away from the heart Valves in the heart are there to keep blood
moving in the right direction
Pulmonary = lungs
*bicuspid valve also known as the MITRAL
valve
Pulmonary Circulation
-Relying on the right ventricle as the pump
-Deoxygenated blood
Systemic Ventricle
-Relying on the left ventricle as the pump
-Deliver all the blood to the various organs; organs then use up oxygen
Red Blood Cell
-Has no mitochondria, so it is not really using oxygen
-No nucleus
-Made for the purpose of carrying around oxygen