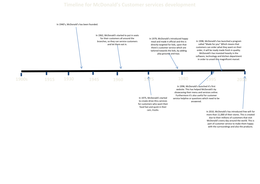
Macy Parsons
Unit 10
Fire tetrahedron
A tetrahedron is a four faced geometric shape resembling
a pyramid. It points to the four components necessary for
a fire to occur—fuel, heat, oxygen, and a chemical chain
reaction—all are represented by the faces of the fire
tetrahedron. The fire will extinguish (go out) if any one of
these necessary components is removed. Research has
shown that four necessary ingredients must exist for fire
to occur, and the fire tetrahedron visually expresses these requirements.
Case study- Australian wildfires
Bushfires in Australia are not uncommon due to the sheer heat of the
continent, however, in recent years of a warming planet, these fires are
becoming more regular, larger, and more dangerous. The ignition of these
wildfires is mostly unintentional from overheating or lightning strikes with
the odd occasion of deliberate ignition. These fires usually spread
hundreds of feet and meet civilised areas, the fire brigade having the
struggle to put them out. Possibly this is due to a constant heat or the
flammability of secondary sources of ignition. Furthermore, the released
gases and smoke caused from the fires may signify incomplete
combustion from burnt fuels or a release of toxic gas. By researching and
establishing data of this as a case study, determining these factors should
indicate to a source of ignition and therefore predicted outcome
(hypothesis).
Primary and secondary sources of ignition
A primary source of ignition is what initially sets
off the fire, the origin cause. Generally, the
primary sources of ignition for fires include open
flames, impact sparks, electrostatic discharge,
cigarettes/matches, vehicles, localised heating,
etc... For the Australian bushfires, the non-
deliberate fires are common on the continent due
to the rising levels of CO2 warming the planet. This has caused Australia to
become significantly hotter in their ‘fire season,’ in addition, this year a
natural whether phenomenon (Indian ocean dipole) has caused hot and
dry spells across the country. Due to the scorching heats, forest fires and
bush fires happen more regularly, having killed 33 people this year. Some
more factors –other than hot weather- have been identified which have
Unit 10
Fire tetrahedron
A tetrahedron is a four faced geometric shape resembling
a pyramid. It points to the four components necessary for
a fire to occur—fuel, heat, oxygen, and a chemical chain
reaction—all are represented by the faces of the fire
tetrahedron. The fire will extinguish (go out) if any one of
these necessary components is removed. Research has
shown that four necessary ingredients must exist for fire
to occur, and the fire tetrahedron visually expresses these requirements.
Case study- Australian wildfires
Bushfires in Australia are not uncommon due to the sheer heat of the
continent, however, in recent years of a warming planet, these fires are
becoming more regular, larger, and more dangerous. The ignition of these
wildfires is mostly unintentional from overheating or lightning strikes with
the odd occasion of deliberate ignition. These fires usually spread
hundreds of feet and meet civilised areas, the fire brigade having the
struggle to put them out. Possibly this is due to a constant heat or the
flammability of secondary sources of ignition. Furthermore, the released
gases and smoke caused from the fires may signify incomplete
combustion from burnt fuels or a release of toxic gas. By researching and
establishing data of this as a case study, determining these factors should
indicate to a source of ignition and therefore predicted outcome
(hypothesis).
Primary and secondary sources of ignition
A primary source of ignition is what initially sets
off the fire, the origin cause. Generally, the
primary sources of ignition for fires include open
flames, impact sparks, electrostatic discharge,
cigarettes/matches, vehicles, localised heating,
etc... For the Australian bushfires, the non-
deliberate fires are common on the continent due
to the rising levels of CO2 warming the planet. This has caused Australia to
become significantly hotter in their ‘fire season,’ in addition, this year a
natural whether phenomenon (Indian ocean dipole) has caused hot and
dry spells across the country. Due to the scorching heats, forest fires and
bush fires happen more regularly, having killed 33 people this year. Some
more factors –other than hot weather- have been identified which have