5,9(9.1-9.3,9.5-9.8),10(10.1-10.3,10.7-10.10,10.13),11(11.12,11.13),24,28(28.5-28.7)
19 jan 2024 Lecture 7: Chapter 9
9.1 Mutations and Mutants
Bacteria can exchange genes
Horizontal gene transfer = movement of genes between cells other than reproduction
Mutation = heritable change in genome
- can lead to a change in properties of an organism
- some beneficial, some detrimental, most have no effect
● Exponential growth in Prok accumulates mutations quickly
● Horizontal gene transfer (genetic exchange) generates much larger changes
● Mutations and genetic exchange fuel evolution
Genomes of cells: double-stranded DNA
Viral genomes (virus): double or single stranded DNA or RNA
Wild type strain = isolated from nature (naturally occurring form)
- wild type can also refer to just one gene
Mutant
● a cell or virus derived from wild type that carries a nucleotide sequence (genotype)
change
- genotype designated by 3 lowercase letters (followed by capital) (e.g. hisC)
- mutations designated hisC1, hisC2, etc
● Observable properties (phenotype) may also be altered
- phenotype designated by capital letter and 2 lowercase letters, then +/-
(e.g. His+)
- the hisC gene of E. coli encodes a protein called HisC that functions in
biosynthesis of the amino acid histidine
- +/- refers to if the property is present or absent
● Can be obtained from either wild-type or parental strain (derived from wild-type)
,Isolation of Mutants: screening versus selection
● Selectable mutations confer an advantage on organisms possessing them
- under certain environmental conditions, progeny cells outgrow and replace
parent
- example: antibiotic resistance
→ : An antibiotic-resistant mutant can grow in the presence of an antibiotic
that inhibits or kills the parent
- Relatively easy to detect
- powerful genetic tool
● Non Selectable mutations do not confer an advantage, even though they may lead
to phenotypic change
- example: color loss in a pigmented organism
- requires laborious, time consuming screening (examining large numbers and
looking for differences)
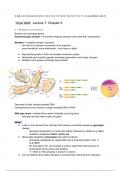
a) antibiotic resistance (due to mutant)
b) non selectable mutation
UV radiation-induced non pigmented mutants
c) colonies of mutants
pink is wild type
top is mutant
- understanding physiology is key to designing genetic screens
- selection is preferred whenever possible
Isolation of Nutritional Auxotrophs
● Replica plating screens for nutritionally defective mutants
- transfer colonies from master plate
- Inability of colony to grow medium lacking a nutrient indicates mutation
- colony on master plate is picked, purified and characterized
● Auxotroph has an additional nutritional requirement for growth above that of the wild
type or parental strain from which it was derived → compared with prototroph (wild
type/parental strain)
→ extra nutrient requirement is His if it is His–
● Complementation = isolation of several strain followed by comparative genetic
analyses
● Selection: The term "selection" is used in various contexts, such as natural selection in biology, selection
of candidates for a job, or selection of materials for a specific purpose.
● Screening: "Screening" is often used in the context of evaluating or examining a group to identify those
that meet certain criteria, whether it's in genetics, medical tests, or job applications.
,9.2 Molecular Basis of mutation
Spontaneous or Induced:
Spontaneous mutations
- occur without external intervention
- most result from occasional errors by DNA polymerase during replication
Induced mutations
- caused due to environment or deliberately (intentionally)
- can result from exposure to natural radiation or chemicals that chemically modify
DNA
Point mutations
- change only 1 base pair
- occur via single base-pair substitution
- phenotypic change depends on location of mutation
Base-pair Substitutions: Missense, Nonsense and Silent
- not all mutations change polypeptides
Point mutations
= change in a single base pair
● involves base substitution
●
● Transition = change of a pyrimidine (C,T) to another pyrimidine OR a purine to
another purine (A,G)
→ more common
Pyrimidine → single ring structure (C,T,U)
Purines → double ring structure (A,G)
● Transversion = change of pyrimidine to a purine or vice versa
Silent mutation = those that do not alter the amino acid sequence
even though base seq has changed
, Missense mutation = base substitution where 1 amino acid change results → inhibitory or
neutral effect
- Sickle cell disease → mutation in B globin gene → change in 6st amino acid →
glutamic to valine → alters structure/function of hemoglobin protein → under
conditions of low oxygen, red blood cell has sickle shape
- not all lead to nonfunction
Nonsense mutation = Involve change from codon that results in a STOP sign → inhibitory
effect
- typically results in truncated (incomplete) protein that lacks normal activity
Frameshift mutation = addition or deletion of number of nucleotides that is not divisible by 3
→ shifts the reading frame → completely different amino acids
- often complete loss of gene function
- can be lethal
- may arise from errors during genetic recombination
- large insertions may be due to transposable elements
Neutral mutation = when a missense mutation has no effect on protein function / also silence
mutations
9.3 Reversions and Mutation rates
Mutation rates depend on frequency of DNA changes and efficiency of DNA repair
Reversions (back mutations) and Suppressors
Wild Type → relatively prevalent genotype → most frequent
Forward mutation → changes WT genotype into some new variation
Reverse mutation / Reversion → changes a mutant allele back to the WT
- occurs because point mutations are typically reversible
- Revertant = strain in which original phenotype is restored
● Same-site revertant: Mutation is at the same site as original mutation
● Second-site revertant: Mutation is at a different site in the DNA that restores
wild-type if functions as suppressor mutation compensating for the original
effect
- mutation somewhere else in the same gene that restores the function
- mutation in another gene that restores function
- mutation in another gene that results in production of an enzyme to
replace a nonfunctional gene
Suppressor mutations = this type of mutation acts to suppress the phenotypic effects of
another mutation
- different than reversion → because it occurs at a different site in DNA from the first
mutation
Suppressors best illustrated by tRNA mutations
● Nonsense mutations can be suppressed by changing anticodon sequence to
recognize stop code (suppressor tRNA)
19 jan 2024 Lecture 7: Chapter 9
9.1 Mutations and Mutants
Bacteria can exchange genes
Horizontal gene transfer = movement of genes between cells other than reproduction
Mutation = heritable change in genome
- can lead to a change in properties of an organism
- some beneficial, some detrimental, most have no effect
● Exponential growth in Prok accumulates mutations quickly
● Horizontal gene transfer (genetic exchange) generates much larger changes
● Mutations and genetic exchange fuel evolution
Genomes of cells: double-stranded DNA
Viral genomes (virus): double or single stranded DNA or RNA
Wild type strain = isolated from nature (naturally occurring form)
- wild type can also refer to just one gene
Mutant
● a cell or virus derived from wild type that carries a nucleotide sequence (genotype)
change
- genotype designated by 3 lowercase letters (followed by capital) (e.g. hisC)
- mutations designated hisC1, hisC2, etc
● Observable properties (phenotype) may also be altered
- phenotype designated by capital letter and 2 lowercase letters, then +/-
(e.g. His+)
- the hisC gene of E. coli encodes a protein called HisC that functions in
biosynthesis of the amino acid histidine
- +/- refers to if the property is present or absent
● Can be obtained from either wild-type or parental strain (derived from wild-type)
,Isolation of Mutants: screening versus selection
● Selectable mutations confer an advantage on organisms possessing them
- under certain environmental conditions, progeny cells outgrow and replace
parent
- example: antibiotic resistance
→ : An antibiotic-resistant mutant can grow in the presence of an antibiotic
that inhibits or kills the parent
- Relatively easy to detect
- powerful genetic tool
● Non Selectable mutations do not confer an advantage, even though they may lead
to phenotypic change
- example: color loss in a pigmented organism
- requires laborious, time consuming screening (examining large numbers and
looking for differences)
a) antibiotic resistance (due to mutant)
b) non selectable mutation
UV radiation-induced non pigmented mutants
c) colonies of mutants
pink is wild type
top is mutant
- understanding physiology is key to designing genetic screens
- selection is preferred whenever possible
Isolation of Nutritional Auxotrophs
● Replica plating screens for nutritionally defective mutants
- transfer colonies from master plate
- Inability of colony to grow medium lacking a nutrient indicates mutation
- colony on master plate is picked, purified and characterized
● Auxotroph has an additional nutritional requirement for growth above that of the wild
type or parental strain from which it was derived → compared with prototroph (wild
type/parental strain)
→ extra nutrient requirement is His if it is His–
● Complementation = isolation of several strain followed by comparative genetic
analyses
● Selection: The term "selection" is used in various contexts, such as natural selection in biology, selection
of candidates for a job, or selection of materials for a specific purpose.
● Screening: "Screening" is often used in the context of evaluating or examining a group to identify those
that meet certain criteria, whether it's in genetics, medical tests, or job applications.
,9.2 Molecular Basis of mutation
Spontaneous or Induced:
Spontaneous mutations
- occur without external intervention
- most result from occasional errors by DNA polymerase during replication
Induced mutations
- caused due to environment or deliberately (intentionally)
- can result from exposure to natural radiation or chemicals that chemically modify
DNA
Point mutations
- change only 1 base pair
- occur via single base-pair substitution
- phenotypic change depends on location of mutation
Base-pair Substitutions: Missense, Nonsense and Silent
- not all mutations change polypeptides
Point mutations
= change in a single base pair
● involves base substitution
●
● Transition = change of a pyrimidine (C,T) to another pyrimidine OR a purine to
another purine (A,G)
→ more common
Pyrimidine → single ring structure (C,T,U)
Purines → double ring structure (A,G)
● Transversion = change of pyrimidine to a purine or vice versa
Silent mutation = those that do not alter the amino acid sequence
even though base seq has changed
, Missense mutation = base substitution where 1 amino acid change results → inhibitory or
neutral effect
- Sickle cell disease → mutation in B globin gene → change in 6st amino acid →
glutamic to valine → alters structure/function of hemoglobin protein → under
conditions of low oxygen, red blood cell has sickle shape
- not all lead to nonfunction
Nonsense mutation = Involve change from codon that results in a STOP sign → inhibitory
effect
- typically results in truncated (incomplete) protein that lacks normal activity
Frameshift mutation = addition or deletion of number of nucleotides that is not divisible by 3
→ shifts the reading frame → completely different amino acids
- often complete loss of gene function
- can be lethal
- may arise from errors during genetic recombination
- large insertions may be due to transposable elements
Neutral mutation = when a missense mutation has no effect on protein function / also silence
mutations
9.3 Reversions and Mutation rates
Mutation rates depend on frequency of DNA changes and efficiency of DNA repair
Reversions (back mutations) and Suppressors
Wild Type → relatively prevalent genotype → most frequent
Forward mutation → changes WT genotype into some new variation
Reverse mutation / Reversion → changes a mutant allele back to the WT
- occurs because point mutations are typically reversible
- Revertant = strain in which original phenotype is restored
● Same-site revertant: Mutation is at the same site as original mutation
● Second-site revertant: Mutation is at a different site in the DNA that restores
wild-type if functions as suppressor mutation compensating for the original
effect
- mutation somewhere else in the same gene that restores the function
- mutation in another gene that restores function
- mutation in another gene that results in production of an enzyme to
replace a nonfunctional gene
Suppressor mutations = this type of mutation acts to suppress the phenotypic effects of
another mutation
- different than reversion → because it occurs at a different site in DNA from the first
mutation
Suppressors best illustrated by tRNA mutations
● Nonsense mutations can be suppressed by changing anticodon sequence to
recognize stop code (suppressor tRNA)