The Liver in Health and Disease
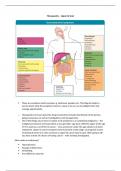
Anatomy of the liver:
Vascular Relationships:
Inflow of blood includes the flow of oxygenated blood through the hepatic artery (from
coeliac trunk) but also the portal vein which drains from the gut, carrying deoxygenated
blood and contains toxins.
Blood flows across the liver and exits through the hepatic vein, which drains into the IVC.
Bile drainage follows same route as blood vessels so forming a portal triad.
Anatomy of the biliary duct:
The gall bladder is there to store and concentrate itself with bile. It is lined by glandular
epithelium which absorb water and contains a thickened muscle layer which contracts to
release bile and bile salts.
, Liver Function:
Vital organ capable of regeneration
Maintaining metabolic homeostasis
Cytoplasm of hepatocytes contains enzymes to enable this – cells have lots of cytoplasm.
Stores nutrients including glycogen, iron, copper and fat-soluble vitamins (ADEK)
Detoxifies harmful substances e.g. hormones, drugs, nitrogenous compounds
Bile synthesis
o Liver is essential for energy production – storage of glycogen so you can release glucose but
also convert glucose back to glycogen (homeostasis).
o It also produces some fats but can oxidise some to produce acetoacetate which is another
molecule which can be fed in to allow gluconeogenesis. Amino acids can also be used as
substrates for gluconeogenesis (feed into Krebs to make OAA (substrate)).
o Also involved in synthesis of non-essential amino acids, complement proteins, plasma
proteins and clotting factors.
o Cholesterol, phospholipids and lipoproteins used by liver to make bile acids which are
precursors to bile salts.
Bile production:
1. Hb broken down in body to produce bilirubin
via biliverdin.
2. Unconjugated bilirubin binds to albumin and
circulates to the liver.
3. In the liver, it is conjugated with glucuronic
acid in hepatocytes.
4. Now its water soluble so is excreted in bile
and enters in gut (bile stored and
concentrated in gall bladder – I cells release
CCK in response to fatty chyme, CCK causes
gall bladder to contract).
Anatomy of the liver:
Vascular Relationships:
Inflow of blood includes the flow of oxygenated blood through the hepatic artery (from
coeliac trunk) but also the portal vein which drains from the gut, carrying deoxygenated
blood and contains toxins.
Blood flows across the liver and exits through the hepatic vein, which drains into the IVC.
Bile drainage follows same route as blood vessels so forming a portal triad.
Anatomy of the biliary duct:
The gall bladder is there to store and concentrate itself with bile. It is lined by glandular
epithelium which absorb water and contains a thickened muscle layer which contracts to
release bile and bile salts.
, Liver Function:
Vital organ capable of regeneration
Maintaining metabolic homeostasis
Cytoplasm of hepatocytes contains enzymes to enable this – cells have lots of cytoplasm.
Stores nutrients including glycogen, iron, copper and fat-soluble vitamins (ADEK)
Detoxifies harmful substances e.g. hormones, drugs, nitrogenous compounds
Bile synthesis
o Liver is essential for energy production – storage of glycogen so you can release glucose but
also convert glucose back to glycogen (homeostasis).
o It also produces some fats but can oxidise some to produce acetoacetate which is another
molecule which can be fed in to allow gluconeogenesis. Amino acids can also be used as
substrates for gluconeogenesis (feed into Krebs to make OAA (substrate)).
o Also involved in synthesis of non-essential amino acids, complement proteins, plasma
proteins and clotting factors.
o Cholesterol, phospholipids and lipoproteins used by liver to make bile acids which are
precursors to bile salts.
Bile production:
1. Hb broken down in body to produce bilirubin
via biliverdin.
2. Unconjugated bilirubin binds to albumin and
circulates to the liver.
3. In the liver, it is conjugated with glucuronic
acid in hepatocytes.
4. Now its water soluble so is excreted in bile
and enters in gut (bile stored and
concentrated in gall bladder – I cells release
CCK in response to fatty chyme, CCK causes
gall bladder to contract).