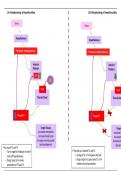
Number code 1- 100 automatically in Devc++
• #include <stdio.h>: This line is a preprocessor directive
• int main(): This line defines the beginning of the main , which is the entry point of a C
program. The function returns an integer int) and does not accept arguments
• printf("Enter a number (type 0 to display numbers from 1 to
• scanf("%i", &numbers);: Esta línea utiliza to read an integer from the user's input and
stores it in scanf
• if (numbers == 0): This is an statement. It checks if
• printf("The numbers from 1 to is equal to 0 numbers
• for (i = 1; i <= 100; i++): This is a for loop that initializes the variable i to 1, and it
continues as long as i is less than or equal to 100. In each iteration, i is incremented by
1.
• printf("%i\n", i);: Inside the loop, this line uses to print the value of followed by a
newline character, displaying the numbers from 1 to 100.printf i
• else: If the condition in the statement is not met (i.e., is not equal to 0), the program
enters the block. if numbers else
• printf("You did not enter 0, so the numbers won't be displayed.\n");: In the block,
this line displays a message indicating that the numbers won't be displayed because the
user did not enter 0. Else
• return 0;: Finally, the statement exits the function and returns 0, which indicates
successful program execution to the operating system. return main
• #include <stdio.h>: This line is a preprocessor directive
• int main(): This line defines the beginning of the main , which is the entry point of a C
program. The function returns an integer int) and does not accept arguments
• printf("Enter a number (type 0 to display numbers from 1 to
• scanf("%i", &numbers);: Esta línea utiliza to read an integer from the user's input and
stores it in scanf
• if (numbers == 0): This is an statement. It checks if
• printf("The numbers from 1 to is equal to 0 numbers
• for (i = 1; i <= 100; i++): This is a for loop that initializes the variable i to 1, and it
continues as long as i is less than or equal to 100. In each iteration, i is incremented by
1.
• printf("%i\n", i);: Inside the loop, this line uses to print the value of followed by a
newline character, displaying the numbers from 1 to 100.printf i
• else: If the condition in the statement is not met (i.e., is not equal to 0), the program
enters the block. if numbers else
• printf("You did not enter 0, so the numbers won't be displayed.\n");: In the block,
this line displays a message indicating that the numbers won't be displayed because the
user did not enter 0. Else
• return 0;: Finally, the statement exits the function and returns 0, which indicates
successful program execution to the operating system. return main