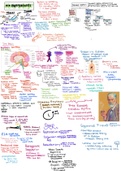
Chap ter-3 Histo ry
Nazis111 and the rise of Hitle r
BIRTH
· OF THE WEIM ER RE .
With the Austi·,· a . ·
PUBLIC: Germ;-iny fought the First World War (1914- 1918) along
Gennan y lnit' .t 11 empire and. ag,Hns• · .t l Iic AIli·es (Engla
11 Y made nd. France a nd Russia). · ._ ·
i:
d eteatin g Gertla 0·11ns l1 y O
ccupym g 1.·ranee and Belgium. However, the Alhes won
•
t,' -
A Nat' nany and th e Central Powers in 191 8.
tona1 Assem bly met . t W . . . .
struct ure Tl . a cimcr and establi shed a dc mocrat1e constitution with a federal
. le repub hc how . . d .
terms it wa f . d ' ever, was not receive well by its own people largely because of the
Germa ns h sldo1 lce to accept . aft er German y's de feat
at the end of the First Wor\d War. Many
. ce at e t 1e new Wem1 er R bl' . 'bl
disgra v·
ersai 11 es.
.
epu ic 1 espons1 e for not only the defeat in the war but the
The Effects of the w _ . . .
psycho} . ar . The war had a devastatmg nnpac t on the entire continent both
11
of the .:};g~ca ~ a nd fin_anc1ally. From being a creditor, Europe becam e a debtor. The suppo rters
nation l' eim_ei Repub hc were criticised and became easy targets of attack
in the conservative
nati al I~t ci r cles. Soldie rs came to be placed above civilians. Aggressive
ona onour becam e impor tant. war propag anda and
P rt·
1
tho •c~l _Radicalism and Economic Crisis: The birth of the Weim er Repub
lic coincided with
S e upr~sm g of the Sparta cist League on the patter n of the Bolshevik Revolu
tion in Russia. The .
P~r~acists found ed the Comm unist Party of Germany.
Politic al radica lisatio n was height ened by the economic crisis of 1923. As
Germany refused to
P~Y the war repara tions, France occupied its leading indust rial area, Ruhr.
Germany retalia ted
with printi ng paper curren cy recklessly. The value of the mark collapsed.
Prices of goods soared.
There was hyper inflati on.
The Years of Depre ssion
1924- 1928 saw some stabili ty, yet it was. built on sand. Germa ny was totally
depen dent on
short- term loans, largel y from the USA. This suppo rt was withd rawn with
the crash in 1929 of
the Wall Street Excha nge. Germa n econo my was hit badly. The middl
e class and working
popul ation was filled with the fear of prolet arianisation.
The Weim er Repub lic had some inhere nt defects :
1. Propo rtiona l Repre sentat ion
2. Articl e 48 - which gave the Presid ent the power s to impos e emergency, suspen d
civil rights
and rule by decree .
HITLER'S RISE TO POWER
Hitler was born in Austr ia in 1889. He earne d many medals for bravery in the First
World War.
The German defeat horrified him. The Treaty of Versailles made him furious. He
joined the
German Workers Party and renamed it National Socialist Germa n Workers' Party.
This later
came to be known as the Nazi Party.
Nazism became a mass movement only during the Great Depression. The Nazi pro~a
ganda
stirred hopes of a better future. Hitler was a powerful and effective speaker. He pronu
sed th
people a strong nation where all would get employment
Nazis111 and the rise of Hitle r
BIRTH
· OF THE WEIM ER RE .
With the Austi·,· a . ·
PUBLIC: Germ;-iny fought the First World War (1914- 1918) along
Gennan y lnit' .t 11 empire and. ag,Hns• · .t l Iic AIli·es (Engla
11 Y made nd. France a nd Russia). · ._ ·
i:
d eteatin g Gertla 0·11ns l1 y O
ccupym g 1.·ranee and Belgium. However, the Alhes won
•
t,' -
A Nat' nany and th e Central Powers in 191 8.
tona1 Assem bly met . t W . . . .
struct ure Tl . a cimcr and establi shed a dc mocrat1e constitution with a federal
. le repub hc how . . d .
terms it wa f . d ' ever, was not receive well by its own people largely because of the
Germa ns h sldo1 lce to accept . aft er German y's de feat
at the end of the First Wor\d War. Many
. ce at e t 1e new Wem1 er R bl' . 'bl
disgra v·
ersai 11 es.
.
epu ic 1 espons1 e for not only the defeat in the war but the
The Effects of the w _ . . .
psycho} . ar . The war had a devastatmg nnpac t on the entire continent both
11
of the .:};g~ca ~ a nd fin_anc1ally. From being a creditor, Europe becam e a debtor. The suppo rters
nation l' eim_ei Repub hc were criticised and became easy targets of attack
in the conservative
nati al I~t ci r cles. Soldie rs came to be placed above civilians. Aggressive
ona onour becam e impor tant. war propag anda and
P rt·
1
tho •c~l _Radicalism and Economic Crisis: The birth of the Weim er Repub
lic coincided with
S e upr~sm g of the Sparta cist League on the patter n of the Bolshevik Revolu
tion in Russia. The .
P~r~acists found ed the Comm unist Party of Germany.
Politic al radica lisatio n was height ened by the economic crisis of 1923. As
Germany refused to
P~Y the war repara tions, France occupied its leading indust rial area, Ruhr.
Germany retalia ted
with printi ng paper curren cy recklessly. The value of the mark collapsed.
Prices of goods soared.
There was hyper inflati on.
The Years of Depre ssion
1924- 1928 saw some stabili ty, yet it was. built on sand. Germa ny was totally
depen dent on
short- term loans, largel y from the USA. This suppo rt was withd rawn with
the crash in 1929 of
the Wall Street Excha nge. Germa n econo my was hit badly. The middl
e class and working
popul ation was filled with the fear of prolet arianisation.
The Weim er Repub lic had some inhere nt defects :
1. Propo rtiona l Repre sentat ion
2. Articl e 48 - which gave the Presid ent the power s to impos e emergency, suspen d
civil rights
and rule by decree .
HITLER'S RISE TO POWER
Hitler was born in Austr ia in 1889. He earne d many medals for bravery in the First
World War.
The German defeat horrified him. The Treaty of Versailles made him furious. He
joined the
German Workers Party and renamed it National Socialist Germa n Workers' Party.
This later
came to be known as the Nazi Party.
Nazism became a mass movement only during the Great Depression. The Nazi pro~a
ganda
stirred hopes of a better future. Hitler was a powerful and effective speaker. He pronu
sed th
people a strong nation where all would get employment