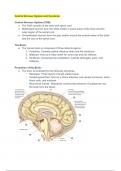
Central Nervous System and Cerebrum
Central Nervous System (CNS):
● The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord.
● Myelinated neurons form the white matter in some areas of the brain and the
outer region of the spinal cord.
● Unmyelinated neurons form the gray matter around the outside areas of the brain
and the core of the spinal cord.
The Brain:
● The human brain is composed of three distinct regions:
1. Forebrain: Contains paired olfactory lobes and the cerebrum.
2. Midbrain: Acts as a relay center for some eye and ear reflexes.
3. Hindbrain: Comprises the cerebellum, medulla oblongata, pons, and
midbrain.
Protection of the Brain:
● The brain is protected by the following structures:
○ Meninges: Three layers of tough elastic tissue.
○ Cerebrospinal fluid: Acts as a shock absorber and carries hormones, white
blood cells, and nutrients.
○ Blood-brain barrier: Selectively controls the entrance of substances into
the brain from the blood.
Central Nervous System (CNS):
● The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord.
● Myelinated neurons form the white matter in some areas of the brain and the
outer region of the spinal cord.
● Unmyelinated neurons form the gray matter around the outside areas of the brain
and the core of the spinal cord.
The Brain:
● The human brain is composed of three distinct regions:
1. Forebrain: Contains paired olfactory lobes and the cerebrum.
2. Midbrain: Acts as a relay center for some eye and ear reflexes.
3. Hindbrain: Comprises the cerebellum, medulla oblongata, pons, and
midbrain.
Protection of the Brain:
● The brain is protected by the following structures:
○ Meninges: Three layers of tough elastic tissue.
○ Cerebrospinal fluid: Acts as a shock absorber and carries hormones, white
blood cells, and nutrients.
○ Blood-brain barrier: Selectively controls the entrance of substances into
the brain from the blood.