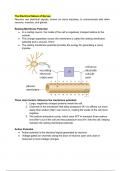
The Electrical Nature of Nerves
Neurons use electrical signals, known as nerve impulses, to communicate with other
neurons, muscles, and glands.
Resting Membrane Potential
● In a resting neuron, the inside of the cell is negatively charged relative to the
outside.
● This charge separation across the membrane is called the resting membrane
potential and is around -70mV.
● The resting membrane potential provides the energy for generating a nerve
impulse.
Three main factors influence the membrane potential:
1. Large, negatively charged proteins inside the cell.
2. Channels in the membrane that allow potassium (K+) to diffuse out more
easily than sodium (Na+) can move in, making the inside of the cell more
negative.
3. The sodium-potassium pump, which uses ATP to transport three sodium
ions (Na+) out of the cell and two potassium ions (K+) into the cell, helping
maintain the resting membrane potential.
Action Potential
● Action potential is the electrical signal generated by neurons.
● Voltage-gated ion channels along the axon of neurons open and close in
response to local voltage changes.
Neurons use electrical signals, known as nerve impulses, to communicate with other
neurons, muscles, and glands.
Resting Membrane Potential
● In a resting neuron, the inside of the cell is negatively charged relative to the
outside.
● This charge separation across the membrane is called the resting membrane
potential and is around -70mV.
● The resting membrane potential provides the energy for generating a nerve
impulse.
Three main factors influence the membrane potential:
1. Large, negatively charged proteins inside the cell.
2. Channels in the membrane that allow potassium (K+) to diffuse out more
easily than sodium (Na+) can move in, making the inside of the cell more
negative.
3. The sodium-potassium pump, which uses ATP to transport three sodium
ions (Na+) out of the cell and two potassium ions (K+) into the cell, helping
maintain the resting membrane potential.
Action Potential
● Action potential is the electrical signal generated by neurons.
● Voltage-gated ion channels along the axon of neurons open and close in
response to local voltage changes.