}
↳
Theory that allows us to count the This is useful for calculating probabilities
number of outcomes of an
experiment .
The basic principle of counting
If experiment 1 has m possible outcomes and for each of these outcomes , experiment 2
has n possible outcomes ,
then the total number of outcomes for the whole experiment is mn .
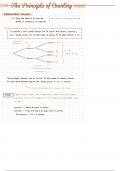
experiment 1
①
y
outcome 1
12 outcomes )
)
outcome 1
"" "
" " °" " ② " "
§
possible outcomes
outcome
③
1
outcome 2
outcome 2
④
experiment 2
( 2 outcomes for each outcome
in experiment 1)
The tree diagram illustrates how we can find the total number of outcomes .
However ,
this could also be calculated the basic outcomes
using counting principle 2×2 4
=
as .
↳
This the theorem
is a
very trivial example but it illustrates
Suppose have each of whom have children If need to choose
Example we 7- women
,
3 .
we
one woman and one of her children for a free holiday ,
how many possible choices
are there ?
Experiment 1 → Choice of the mother ( 7- outcomes )
Experiment 2 → Choice of the child for the chosen mother ( 3 outcomes )
i. Total outcomes = 7×3 =
21 outcomes
,The generalised basic principle of counting
suppose we need to perform r experiments ,
where the first experiment has n
,
outcomes ,
the second experiment has nz Outcomes ,
. . .
,
the rth ( last ) experiment has nr outcomes .
The total number of outcomes of the r experiments is n
,
✗
nzx .
. . ✗ nr .
'
- -
Example A student body consists of 4 freshmen , 3 sophomores , 2
juniors and 5 seniors .
If a student council is to be formed and must consist of 1 person from each
class 14 people on the council in total ) ,
how many different committees can
be formed ? " "
A useful
"
trick
"
to when have AND and
is multiply we
✗
"
to add when we have OR "
.
We require : 1 freshman AND i sophomore AND I
junior AND I senior
From the generalised of possible committees
counting
basic principle : 4×3×2×5 = 120
Example How many 7 -
digit license plates can we make if the first 3
digits are to be letters and
the remaining 4 digits by numbers ? What if repetition of letters and numbers is not allowed ?
Ii ) We have : 26×26 ✗ 26 ✗ 10×10×10×10
= 263 ✗ 104
=
175 760 000 possible license plates
Iii ) In this still the generalised principle of have
case ,
using counting ,
we
26 ✗ 25×24 ✗ 10×9×8×7 =
78 624 000 possible license plates
↑
}
we can't use the one letter
think of how options each
we chose in position 1 ,
many
and so on .
position has available .
, PERMUTATIONS
↳ Deals with ordered
arrangements of objects
First result
If want to arrange objects where each object in every then the number
we n , appears arrangement ,
the number of arrangements we can make is n ! .
'
-
Example How
many different batting orders are possible for a 9-
player baseball team ?
There are 9 ! =
362880 possible batting orders
Example If a student has 4 maths books , 2 chemistry books and 3 biology books ,
how
many
these books bookshelf if the books to the
ways can we
arrange on a
belonging same
subject should each distinct ?
be
grouped together and book is
There are 4 ! arrangements of math books , 2 ! arrangements of Chem books and 3 !
arrangements of
bio books . We then regard each group as an object giving ,
us 3 !
ways to arrange each of the groups .
i. (4! ✗ 2 ! ✗ 3 ! ) ✗ 3 ! =
1728 arrangements
the
I ↑
arranging
each
books within each arranging group
particular subject
second result
If we have n objects with n
, objects identical to each other , nz objects identical to each other ,
nr Objects identical to each other then the number of these objects can be
arranged
ways
- .
,
_
,
is calculated as :
can think of it as
n !
"
"
removing the repetitions
n, ! nz ! .
. .
nr ! I
, Example If we have 5 red balls ,
3 white balls and 6 blue balls ,
how many different ways can
these balls in line ?
we
arrange a
There (5+3+6) ! !
are =
14
= 168168 possible distinct arrangements
5 ! 3 ! 6 ! 5 ! 3 ! 6!
Further result
The number of permutations of r different objects which are chosen from n objects is
defined as :
npr =
Prn = n In 1) ( n 2)
- -
. . . (n -
r +
1) =
n !
( n -
r )!
L 0 Think of it as we want to select r objects from
a
larger group of n objects and the objects are ordered .
How there to arrange students in from group of
a row
Example many ways are 5 a
10 students ?
10ps = 10 ! =
10 ! =
10×9 ✗ 8×7×6×5 ✗ 4×3×2×1
= 10×9×8×7 ✗ 6 =
30240
(10-5) ! 5
! 5×4×3×2 ✗ 1
COMBINATIONS
↳ Similar to but when not important
permutations , ordering is .
Combination definition
we define the combination where we want to choose r objects from the larger
of objects and the ordering of the objects is not important
group n as :
(f) for
=
n ! r ≤ n
(n -
r )!r!