Accounting → Collecting and delivering information to help stakeholders make better decision
Finance → Ways to raise and invest funds to help stakeholders in their decision making process
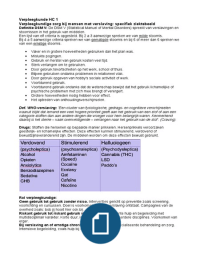
Stakeholders
user group (internal or external) which have an interest within the business
INTERESTS DECISION
Employees future plans, profit whether or not working in the company
Customers reliability, prices whether or not buying goods or services
Lenders receive their money back whether or not lending money
Investors pay for the services supplied whether or not investing
Owners look for profit whether or not investing
Community new workplaces provide economic support
Purpose of a business
satisfy all stakeholders
reaching targets
customer is a king
Financial objectives
main → enhance wealth of its owner
secondary → good working conditions, product quality
Information
Sources
meeting with managers
newspapers
announcements made by the company
internet → reports
Weighing costs and benefits
if costs < benefits then the information should be produced
optimal quantity → when the gap costs - value is at its greatest
Usefulness
Fundamental
Relevance
influencing decision → predict future events and confirm past ones
Materiality → if the omission of a certain information would affect the decision making process
Faithful representation
Complete
free from error
neutral
Introduction 1
, Enhancing
Comparability
Verifiability
Timeliness
Understandability
System
graph LR
id1(Information IDENTIFICATION) --> id2(Information RECORDING) --> id3(Information ANALYSIS)--> id4(Information REPORTING)
Introduction 2
, Management and financial
accounting
Management accounting → information for managers
not highly regulated because managers have the power to decide when to receive the
report
Financial accounting → information for external stakeholders
MANAGEMENT FINANCIAL
Nature of the
Specific purpose (profit of a specific thing) General purpose
reports
Level of detail Very detailed Broad overview
Regulation Unregulated Subject to accounting regulation
Reporting interval As short as required Annual or biannual
Time horizon Projected future information and also past ones Historical
Focus on financial information
Range and quality Financial and non financial information often
emphasis on objective verifiable
of information these information cannot be verified
evidence
Business proprietorship
Sole proprietorship → 1 person
easy to set up, flexible
BUT unlimited liability
Partnership → ≥ 2 people
easy to set up, spreads burdens
BUT unlimited liability and you have to find partners you get on well
Limited liability company → ∞
limited liability
BUT obligations set up by the company
Management and financial accounting 1