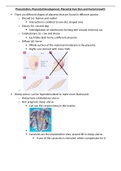
There are different shapes of placenta that are found in different species
o Discoid (a)- human and rodent
Interaction is confined to one disc shaped area
o Zonary (b)- cat and dog
Interdigitation of membranes forming belt around chorionic sac
o Cotyledonary (c)- cow and sheep
Each little blob forms a different placenta
o Diffuse (d)- horse
Whole surface of the maternal membrane is the placenta
Highly vascularised with many folds
o
Sheep uterus- can be hyperstimulated to make more blastocysts
o Sheep have cotyledonary uterus
o Non pregnant sheep uterus
Can see the corpora lutea in the ovaries
Caruncles are the implantation sites, around 80 in sheep uterus
If one of the caruncles is removed, others compensate for it
,
o Caruncles are found on the maternal side
o Cotyledons are found on the foetal side
o Placentome- individual placental unit, a combination of a caruncle and a
cotyledon
Placentation creates a vascular supply to supply the foetus with blood
Interdigitation of foetal material and maternal material in the
caruncle
Trophoblast dips into the caruncles
Maternal side is formed of a capillary bed
Surrounded by epithelia
Comes in in uterine artery, leaves through the uterine vein
Specially adapted to match foetal capillary bed
o In sheep there are a layer of endothelial cells, and then epithelial cells on the
maternal side
On the foetal side there an endothelial and trophoblast layer
Blood has to cross 4 layers from mother to embryo
Different types of placentation can also be described by their histological features