Lecture 6.1 – Photoreception
Objectives
§ Single-lens eye
§ Photoreception
§ The photoreception component
of the retina
§ Photoreceptors
§ Retinal and opsin
§ Glutamate
§ Signalling light
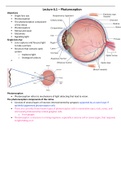
Single-lens Eye
§ Lens captures and focuses light
to take a picture.
§ Structure that contains optic
system
o Captures light.
o Distinguish colours.
§
Photoreception
• Photoreception refers to mechanisms of light detecting that lead to vision.
The photoreception components of the retina
• Consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses supported by an outer layer lf
epithelial pigmented photoreceptor cells.
• There are currently three known types of photoreceptor cells in mammalian eyes; rods, cones, and
intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells.
o From google.
• Photoreceptor: a structure in a living organism, especially a sensory cell or sense organ, that responds
to light falling on it.
Objectives
§ Single-lens eye
§ Photoreception
§ The photoreception component
of the retina
§ Photoreceptors
§ Retinal and opsin
§ Glutamate
§ Signalling light
Single-lens Eye
§ Lens captures and focuses light
to take a picture.
§ Structure that contains optic
system
o Captures light.
o Distinguish colours.
§
Photoreception
• Photoreception refers to mechanisms of light detecting that lead to vision.
The photoreception components of the retina
• Consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses supported by an outer layer lf
epithelial pigmented photoreceptor cells.
• There are currently three known types of photoreceptor cells in mammalian eyes; rods, cones, and
intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells.
o From google.
• Photoreceptor: a structure in a living organism, especially a sensory cell or sense organ, that responds
to light falling on it.