change
Enquiry question 1
> Why are coastal landscapes different & what processes causes these
differences?
Key idea
2B.1 the coast, & wider littoral zone, has distinctive features & landscapes
2B.2 geological structure influences the development of coastal landscapes at a
variety of scales
2B.3 rates of coastal recession & stability depend on lithology & other factors
Detailed content
a. The littoral zone consists of backshore, nearshore & offshore zones, includes a
wide variety of coastal types & is a dynamic zone of rapid change
b. Coasts can be classified by using longer term criteria such as geology &
changes of sea level or shorter-term processes such as inputs from rivers, waves
& tides
c. Rocky coasts (high & low relief) result from resistant geology (withstands erosive
forces of sea, rain & wind), often in a high-energy environment, whereas coastal
plain landscapes (Sandy & estuarine coasts) are found near areas of low relief &
result from supply of sediment from different terrestrial & offshore sources, often
in a low-energy environment
a. Geological structure is responsible for the formation of concordant & discordant
coasts
b. Geological structure influences coastal morphology: Dalmatian & Haff type
concordant coasts & headlands & bays on discordant coasts
c. Geological structure (jointing, dip, faulting, folding) is an important influence on
coastal morphology & erosion rates, & also on the formation of cliff profiles & the
occurrence of micro-features, e.g. caves
a. Bedrock lithology (igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic) & unconsolidated
material (boulder clay) geology are important in understanding rates of coastal
recession
,b. Differential erosion of alternating strata in cliffs (permeable/impermeable,
resistant/less resistant) produces complex cliff profiles & influences recession
rates
c. Vegetation is important in stabilising sandy coastlines through dune successional
development & salt march successional development in estuarine areas
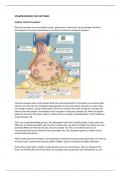
The littoral zone (also known as intertidal zone)
= the area of the shoreline where land is subject to wave action - subdivided
into offshore, nearshore, foreshore & backshore & includes a wide variety of
coastal types, & is a dynamic zone of rapid change.
Backshore = Inshore/Nearshore =
area above the the area of shallow
high tide mark, water between the
not usually low water mark & the
touched by point where waves
waves except in stop having any
major storm influence on the land
events around them.
Foreshore = Offshore = the area beyond
area between the point where waves
high tide & low cease to impact the
tide mark (often seabed – deeper water
seen as the beyond point at which
most important waves begin to break & in
area for marine which activity is limited to
activity). the deposition of sediments.
,Coast is considered a system
Inputs
Marine – waves, tides, storm surges
Atmospheric – weather/climate, climate
change, solar energy
Land – rock type & structure, tectonic
activity
People – human activity, coastal
management
Processes
* Weathering
* Mass movement
* Erosion
* Transportation
* Deposition
Outputs
* Erosional landforms
* Depositional
landforms
* Different types of
coasts
Factors affecting wave energy
- Depth & shape of coastline
- Duration (that wind has blown)
- Fetch (distance wind has blown)
, How coasts vary –
Resistant rock coastlines Coastal plain landscapes (Eastern &
(western & Northern Britain) Southern Britain)
- Rocky coastline of - Consists of younger, weaker
igneous/basalt can sedimentary rocks (chalks,
withstand frequent clays, sand & sandstone)
storms with little erosion - Low flat relief: has a range of
- Also has compacted habitats from tidal creeks,
older sedimentary rocks mud flats, salt marshes &
(such as old sandstone) lagoons, low lying sandy
& metamorphic rocks beaches (some with sand
(slates & schists) dunes)
West coast has higher energy waves & east coast has lower energy waves.
High energy coastlines Low energy coastlines
* Rocky coastlines are * Sandy (sand dunes/beaches)
generally found in high & estuarine (salt
energy environments marches/mudflats) coasts are
generally found in low energy
They tend to be environments
* Stretches of the Atlantic
facing coasts, where the In UK, these tend to be
waves are powerful (large * Stretches of coast where the
fetch) for most of year waves are less powerful or
(Cornwall & NW Scotland) where the coast is sheltered
* Where the rate of erosion from large waves (such as
exceeds the rate of Lincolnshire & Norfolk
deposition * Where the rate of deposition
* Landforms include exceeds the rate of erosion
headlands, cliffs, shoreline * Made up of less resistant rock
platforms (wave-cut * Found in areas of low relief
platforms
* High relief
* Destructive waves Many coasts can be a mixture of high
& low