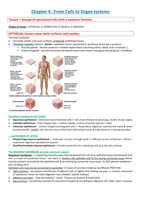
Chapter 16 : The Reproductive Systems
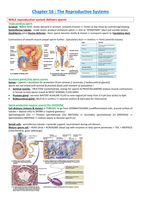
MALE reproductive system delivers sperm
Testes produce sperm
Scrotum : Before birth, testes descend in scrotum (smooth muscle) => Testes at low temp by contracting/relaxing.
Seminiferous tubules : inside testes, produce immature sperm => Join as “EPIDIDYMIS” (duct just outside testes)
(Epididymis joins) Ductus deferens : Here, sperm become motile & stored => transports sperm to Ejaculatory duct.
Contractions of smooth muscle propel sperm further ; Ejaculatory duct => Urethra => Penis (erectile tissues)
Accessory glands help sperm survive
Semen = [sperm + secretions for protection (from seminal // prostrate // bulbourethral glands)]
Sperm are not mixed with seminal & prostate fluids until moment of ejaculation !
Seminal vesicles : FRUCTOSE (carbohydrate, energy for sperm) & PROSTAGLANDINS (induce muscle contractions
in female to help sperm travel) & MOST SEMINAL FLUID (60%)
Prostate gland : secretes WATERY ALKALINE FLUID to raise vaginal pH temp from 3-4 pH (too acidic) to 6pH.
Bulbourethral gland : MUCUS in urethra => cleanses urethra & lubricates for intercourse.
Sperm production requires several CELL DIVISIONS
Cell divisions (mitosis & meiois) in TUBULES, to go from SPERMATOGONIA (undifferentiated cells, around surface of
tubules = diploid cells) to SPERM (= haploid gametes) :
Spermatogonia (2n) => Primary spermatocyte (2n) (MITOSIS) => Secondary spermatocyte (n) (MEIOISIS) =>
Spermatids(n) (MEIOSIS) => mature slowly to become sperm (n)
Sertoli cells : seminiferous tubules =>provide support, nourishment during cell division.
Mature sperm cell = HEAD (dna) + ACROSOME (head cap with enzymes to help sperm penetrate) + TAIL + MIDPIECE
(mitochondria, gives tailenergy).
MALE reproductive system delivers sperm
Testes produce sperm
Scrotum : Before birth, testes descend in scrotum (smooth muscle) => Testes at low temp by contracting/relaxing.
Seminiferous tubules : inside testes, produce immature sperm => Join as “EPIDIDYMIS” (duct just outside testes)
(Epididymis joins) Ductus deferens : Here, sperm become motile & stored => transports sperm to Ejaculatory duct.
Contractions of smooth muscle propel sperm further ; Ejaculatory duct => Urethra => Penis (erectile tissues)
Accessory glands help sperm survive
Semen = [sperm + secretions for protection (from seminal // prostrate // bulbourethral glands)]
Sperm are not mixed with seminal & prostate fluids until moment of ejaculation !
Seminal vesicles : FRUCTOSE (carbohydrate, energy for sperm) & PROSTAGLANDINS (induce muscle contractions
in female to help sperm travel) & MOST SEMINAL FLUID (60%)
Prostate gland : secretes WATERY ALKALINE FLUID to raise vaginal pH temp from 3-4 pH (too acidic) to 6pH.
Bulbourethral gland : MUCUS in urethra => cleanses urethra & lubricates for intercourse.
Sperm production requires several CELL DIVISIONS
Cell divisions (mitosis & meiois) in TUBULES, to go from SPERMATOGONIA (undifferentiated cells, around surface of
tubules = diploid cells) to SPERM (= haploid gametes) :
Spermatogonia (2n) => Primary spermatocyte (2n) (MITOSIS) => Secondary spermatocyte (n) (MEIOISIS) =>
Spermatids(n) (MEIOSIS) => mature slowly to become sperm (n)
Sertoli cells : seminiferous tubules =>provide support, nourishment during cell division.
Mature sperm cell = HEAD (dna) + ACROSOME (head cap with enzymes to help sperm penetrate) + TAIL + MIDPIECE
(mitochondria, gives tailenergy).