Chapter 15 : The Urinary System
The urinary system contributes to HOMEOSTASIS
Excretion = process that removes wastes and excess materials from the body (maintaining homeostatis of water and
solutes in our bodies). Kidneys = Key-organs !
Urinary system = Kidneys + Ureters + Urinary bladder + Urethra
Kidneys regulate WATER LEVELS
~60% of body weight, 2 ½ liters exch with env/day – produce 300 ml/day
Input (food, metabol) MUST = output (urine, lungs, feces..) => kidneys can adjust water secr from ½l/day to 1l/h
Kidneys excrete/regulate NITROGENOUS WASTES AND OTHER SOLUTES
Nitrogenous wastes from amino-acids : from metabolism of proteins => liberates ammonia (toxic to cells but
detoxificated by liver by combining it with CO2 => UREA + WATER).
Excess ions : from food or metabolism of nutrients :
SODIUM & CHLORIDE => both important for volume of extracellular fluid like blood => Blood Vol affects Pressure.
POTASSSIMUM, CALCIUM, HYDROGEN => regulate excretion of these to maintain homeostasis of each one.
Traces of other substances : excreted in PROPORTION to their productionrate/day. eg CREATININE (waste product
of metabolism of creatine phospate = energy source in muscle), waste products that give urine the yellow color.
Creatinine levels in blood & urine used to calculate „creatinine clearance“ (CrCl) index of glomerular filtration rate
GFR = Clinically important parameter of renal function
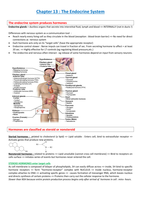
Organs of the urinary system
KIDNEYS = The principal urinary organs
At sides of vertebral column near posterior body wall, dark reddish-brown organ, fist-size, bean-shaped.
RENAL ARTERY + RENAL VEIN connect to AORTA + INFERIOR VENA CAVA. Main parts :
Medulla : inner piramyd-shaped zones of dense tissues ‘renal piramyds’
Cortex : outer zone
Renal pelvis : hollow space inside => urine collected after formed.
Nephrons : long, thin, tubular structures in cortex & medulla
Collecting duct : common final sections of the nephrons => urine delivered to renal pelvis.
URETERS transport urine to the bladder
Renal pelvis => Ureter = muscular tube, transports urine to bladder by Peristaltic waves of smooth muscle contraction
(every 10-15 secs) along ureters (25cm) to bladder.
URINARY BLADDER stores urine
Three layers of smooth muscle, lined at inside with epithelial cells. Can hold 600-1000 ml but women have smaller
The urinary system contributes to HOMEOSTASIS
Excretion = process that removes wastes and excess materials from the body (maintaining homeostatis of water and
solutes in our bodies). Kidneys = Key-organs !
Urinary system = Kidneys + Ureters + Urinary bladder + Urethra
Kidneys regulate WATER LEVELS
~60% of body weight, 2 ½ liters exch with env/day – produce 300 ml/day
Input (food, metabol) MUST = output (urine, lungs, feces..) => kidneys can adjust water secr from ½l/day to 1l/h
Kidneys excrete/regulate NITROGENOUS WASTES AND OTHER SOLUTES
Nitrogenous wastes from amino-acids : from metabolism of proteins => liberates ammonia (toxic to cells but
detoxificated by liver by combining it with CO2 => UREA + WATER).
Excess ions : from food or metabolism of nutrients :
SODIUM & CHLORIDE => both important for volume of extracellular fluid like blood => Blood Vol affects Pressure.
POTASSSIMUM, CALCIUM, HYDROGEN => regulate excretion of these to maintain homeostasis of each one.
Traces of other substances : excreted in PROPORTION to their productionrate/day. eg CREATININE (waste product
of metabolism of creatine phospate = energy source in muscle), waste products that give urine the yellow color.
Creatinine levels in blood & urine used to calculate „creatinine clearance“ (CrCl) index of glomerular filtration rate
GFR = Clinically important parameter of renal function
Organs of the urinary system
KIDNEYS = The principal urinary organs
At sides of vertebral column near posterior body wall, dark reddish-brown organ, fist-size, bean-shaped.
RENAL ARTERY + RENAL VEIN connect to AORTA + INFERIOR VENA CAVA. Main parts :
Medulla : inner piramyd-shaped zones of dense tissues ‘renal piramyds’
Cortex : outer zone
Renal pelvis : hollow space inside => urine collected after formed.
Nephrons : long, thin, tubular structures in cortex & medulla
Collecting duct : common final sections of the nephrons => urine delivered to renal pelvis.
URETERS transport urine to the bladder
Renal pelvis => Ureter = muscular tube, transports urine to bladder by Peristaltic waves of smooth muscle contraction
(every 10-15 secs) along ureters (25cm) to bladder.
URINARY BLADDER stores urine
Three layers of smooth muscle, lined at inside with epithelial cells. Can hold 600-1000 ml but women have smaller