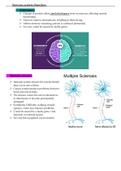
Nervous system disorders.
- Alzheimer’s:
➢ Clumps of protein called amyloid plaques form on neurons, affecting normal
functioning.
➢ Neurons cannot communicate, resulting in them dying.
➢ Affects memory reasoning, person is confused {dementia}.
➢ No cure, could be caused by faulty genes.
- Multiple sclerosis:
➢ Immune system attracts the myelin sheath
that covers nerve fibres.
➢ Causes communication problems between
brain and rest of body.
➢ The disease causes the nerves themselves
to deteriorate or become permanently
damaged.
➢ Symptoms: Difficulty walking; muscle
spasms; vision loss, balance problems.
➢ Could be caused by a faulty gene, viral
infection or external factors.
➢ No cure but symptoms can be treated.
, Injuries to the brain.
- Nerves in the central nervous system {CNS} cannot regenerate.
- Nerve in the peripheral nervous system {PNS} is able to regenerate.
- Traumatic brain injury result from external force.
- This can lead to a concussion: Temporary and headaches, loss of coordination and
concentration, balance and memory problems.
- Force to the lead can lead to hemorrhaging swelling of the brain and tearing of the
meninges.
Spinal cord injuries.
¬ Vertebrae protect the spinal cord.
¬ Due to accidents & sport injuries the vertebrae may become dislodged broken or
fractured resulting in damage to the spinal cord.
¬ Results of spinal injuries depends on what level the spinal cord is damaged.
¬ Complete injuries occur when there is no movement or sensation at all.
¬ Incomplete is when there is still some functioning.
¬ Quadriplegia or paraplegia may result.
¬ Treatment is difficult since CNS neurons cannot regenerate.
¬ Stem cell research is being done.
Effects drugs have on the nervous system.
➢ A drug can be natural, or man-made and changes a person’s behaviour, thinking and
emotions.
➢ Drugs can be stimulants, depressants and hallucinogens.
➢ Some drugs can overlap the above three categories.
➢ Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, appetite, sleep, sexual desire.
➢ Lack of serotonin thus causes depression insomnia.
➢ Dopamine stimulates feelings of happiness and well-being
➢ Lack of dopamine causes lack of focuses.
- Alzheimer’s:
➢ Clumps of protein called amyloid plaques form on neurons, affecting normal
functioning.
➢ Neurons cannot communicate, resulting in them dying.
➢ Affects memory reasoning, person is confused {dementia}.
➢ No cure, could be caused by faulty genes.
- Multiple sclerosis:
➢ Immune system attracts the myelin sheath
that covers nerve fibres.
➢ Causes communication problems between
brain and rest of body.
➢ The disease causes the nerves themselves
to deteriorate or become permanently
damaged.
➢ Symptoms: Difficulty walking; muscle
spasms; vision loss, balance problems.
➢ Could be caused by a faulty gene, viral
infection or external factors.
➢ No cure but symptoms can be treated.
, Injuries to the brain.
- Nerves in the central nervous system {CNS} cannot regenerate.
- Nerve in the peripheral nervous system {PNS} is able to regenerate.
- Traumatic brain injury result from external force.
- This can lead to a concussion: Temporary and headaches, loss of coordination and
concentration, balance and memory problems.
- Force to the lead can lead to hemorrhaging swelling of the brain and tearing of the
meninges.
Spinal cord injuries.
¬ Vertebrae protect the spinal cord.
¬ Due to accidents & sport injuries the vertebrae may become dislodged broken or
fractured resulting in damage to the spinal cord.
¬ Results of spinal injuries depends on what level the spinal cord is damaged.
¬ Complete injuries occur when there is no movement or sensation at all.
¬ Incomplete is when there is still some functioning.
¬ Quadriplegia or paraplegia may result.
¬ Treatment is difficult since CNS neurons cannot regenerate.
¬ Stem cell research is being done.
Effects drugs have on the nervous system.
➢ A drug can be natural, or man-made and changes a person’s behaviour, thinking and
emotions.
➢ Drugs can be stimulants, depressants and hallucinogens.
➢ Some drugs can overlap the above three categories.
➢ Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, appetite, sleep, sexual desire.
➢ Lack of serotonin thus causes depression insomnia.
➢ Dopamine stimulates feelings of happiness and well-being
➢ Lack of dopamine causes lack of focuses.