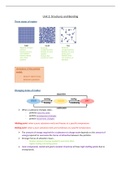
Three states of matter
Regularly arranged Randomly Randomly
particles arranged particles arranged particles
Particles are very Particles are close Particles are much
close together together further apart
Particles vibrate Particles flow Particles move
about fixed around each other very quickly in all
positions directions
Limitations of the particle
model:
- Doesn’t take forces
between particles
into account
Changing states of matter
deposition
melting boiling
SOLID LIQUID GAS
freezing condensing
sublimation
When a substance changes state…
- particles stay the same
- particle arrangement changes
- particle movement changes
Melting point: when a pure substance melts and freezes at a specific temperature.
Boiling point: when a pure substance boils and condenses at a specific temperature.
The amount of energy required for a substance to change state depends on the amount of
energy required to overcome the forces of attraction between the particles.
Stronger forces of attraction mean…
- Greater amount of energy needed to overcome them
- Higher melting and boiling points
Ionic compounds, metals and giant covalent structures all have high melting points due to
strong bonds.
, Identifying the State of a Substance
The MPT and BPT of a substance can be used to identify its state at a given temperature :
Example:
What is the state of each element at 25C̊?
Element Melting point (C̊) Boiling point (C̊)
Fluorine -220 -188
Chlorine -102 -34
Bromine -7 59
Iodine 114 184
25C̊ is below the melting point 25C̊ is below the boiling point but 25C̊ is above the boiling points of
of iodine, so it will be a solid. above the melting point of fluorine and chlorine, so they will
bromine, so it will be liquid. be gases.
State symbols
Chemical equations sum up what State symbol State of substance
happens in reactions. (s) Solid
State symbols show the states of each (l) Liquid
substance involved. (g) Gas
(aq) Aqueous (dissolved in water)
Chemical bonding
Chemical reactions are all to do with the behaviours of outer electrons of an element
Atoms “want” to become stable
The three types of bonding are:
- Ionic bonding
Occurs between metals and non-metals
The metal transfers some of its outer electrons to a non-metal
- Covalent bonding
Occurs between non-metals when they share electrons
- Metallic bonding
Occurs within metals when the outer electron is free to move throughout the whole
structure
Key Definitions
Compound = made of more than one type of atom
Molecules = two or more of the same type of atom bonded
Elements = one atom only